Retinotopic mapping with spin echo BOLD at 7T
- PMID: 20656431
- PMCID: PMC2963715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2010.06.001
Retinotopic mapping with spin echo BOLD at 7T
Abstract
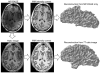
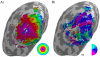
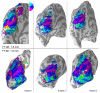
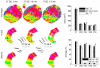
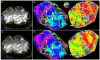
For blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) functional MRI experiments, contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) increases with increasing field strength for both gradient echo (GE) and spin echo (SE) BOLD techniques. However, susceptibility artifacts and nonuniform coil sensitivity profiles complicate large field-of-view fMRI experiments (e.g., experiments covering multiple visual areas instead of focusing on a single cortical region). Here, we use SE BOLD to acquire retinotopic mapping data in early visual areas, testing the feasibility of SE BOLD experiments spanning multiple cortical areas at 7T. We also use a recently developed method for normalizing signal intensity in T(1)-weighted anatomical images to enable automated segmentation of the cortical gray matter for scans acquired at 7T with either surface or volume coils. We find that the CNR of the 7T GE data (average single-voxel, single-scan stimulus coherence: 0.41) is almost twice that of the 3T GE BOLD data (average coherence: 0.25), with the CNR of the SE BOLD data (average coherence: 0.23) comparable to that of the 3T GE data. Repeated measurements in individual subjects find that maps acquired with 1.8-mm resolution at 3T and 7T with GE BOLD and at 7T with SE BOLD show no systematic differences in either the area or the boundary locations for V1, V2 and V3, demonstrating the feasibility of high-resolution SE BOLD experiments with good sensitivity throughout multiple visual areas.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterizing contrast origins and noise contribution in spin-echo EPI BOLD at 3 T.Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Apr;57:328-336. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30439514
-
Comparison of BOLD, diffusion-weighted fMRI and ADC-fMRI for stimulation of the primary visual system with a block paradigm.Magn Reson Imaging. 2017 Jun;39:123-131. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.01.022. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28163122
-
Comparison of 3T and 7T ASL techniques for concurrent functional perfusion and BOLD studies.Neuroimage. 2017 Aug 1;156:363-376. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.05.038. Epub 2017 May 19. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 28528845
-
Spin-echo fMRI: The poor relation?Neuroimage. 2012 Aug 15;62(2):1109-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.003. Epub 2012 Jan 8. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22245351 Review.
-
Exploring structure and function of sensory cortex with 7T MRI.Neuroimage. 2018 Jan 1;164:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.01.081. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28161312 Review.
Cited by
-
7 Tesla and Beyond: Advanced Methods and Clinical Applications in Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Invest Radiol. 2021 Nov 1;56(11):705-725. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000820. Invest Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34510098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of visual cortex activation in patients with anterior visual pathway lesions.Neural Regen Res. 2012 Mar 25;7(9):692-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.09.009. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25745465 Free PMC article.
-
Multishot versus single-shot pulse sequences in very high field fMRI: a comparison using retinotopic mapping.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034626. Epub 2012 Apr 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22514646 Free PMC article.
-
Columnar organization of mid-spectral and end-spectral hue preferences in human visual cortex.Neuroimage. 2018 Nov 1;181:748-759. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.07.053. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 30053514 Free PMC article.
-
Relation between palm and finger cortical representations in primary somatosensory cortex: A 7T fMRI study.Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 May;42(7):2262-2277. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25365. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 33621380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ugurbil K, Adriany G, Andersen P, et al. Ultrahigh field magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging. 2003;21(10):1263–1281. - PubMed
-
- Yacoub E, Shmuel A, Pfeuffer J, et al. Imaging brain function in humans at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med. 2001;45(4):588–594. - PubMed
-
- Yacoub E, Duong TQ, Van de Moortele P-F, et al. Spin-echo fMRI in humans using high spatial resolutions and high magnetic fields. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2003;49:655–664. - PubMed
-
- Vaughan JT, Garwood M, Collins CM, et al. 7T vs. 4T: RF power; homogeneity; and signal-to-noise comparison in head images. Mag Reson Med. 2001;46:24–30. - PubMed
-
- Thulborn KR, Waterton JC, Matthews PM, Radda GK. Oxygenation dependence of hte transverse relaxation time of water protons i nwhole blood at high field. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - General Subjects. 1982;714(2):265–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

