A population genetics-based and phylogenetic approach to understanding the evolution of virulence in the genus Listeria
- PMID: 20656873
- PMCID: PMC2937515
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00447-10
A population genetics-based and phylogenetic approach to understanding the evolution of virulence in the genus Listeria
Abstract
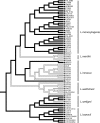
The genus Listeria includes (i) the opportunistic pathogens L. monocytogenes and L. ivanovii, (ii) the saprotrophs L. innocua, L. marthii, and L. welshimeri, and (iii) L. seeligeri, an apparent saprotroph that nevertheless typically contains the prfA virulence gene cluster. A novel 10-loci multilocus sequence typing scheme was developed and used to characterize 67 isolates representing six Listeria spp. (excluding L. grayi) in order to (i) provide an improved understanding of the phylogeny and evolution of the genus Listeria and (ii) use Listeria as a model to study the evolution of pathogenicity in opportunistic environmental pathogens. Phylogenetic analyses identified six well-supported Listeria species that group into two main subdivisions, with each subdivision containing strains with and without the prfA virulence gene cluster. Stochastic character mapping and phylogenetic analysis of hly, a gene in the prfA cluster, suggest that the common ancestor of the genus Listeria contained the prfA virulence gene cluster and that this cluster was lost at least five times during the evolution of Listeria, yielding multiple distinct saprotrophic clades. L. welshimeri, which appears to represent the most ancient clade that arose from an ancestor with a prfA cluster deletion, shows a considerably lower average sequence divergence than other Listeria species, suggesting a population bottleneck and a putatively different ecology than other saprotrophic Listeria species. Overall, our data suggest that, for some pathogens, loss of virulence genes may represent a selective advantage, possibly by facilitating adaptation to a specific ecological niche.
Figures


References
-
- Achtman, M. 2008. Evolution, population structure, and phylogeography of genetically monomorphic bacterial pathogens. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 62:53-70. - PubMed
-
- Achtman, M., G. Morelli, P. Zhu, T. Wirth, I. Diehl, B. Kusecek, A. J. Vogler, D. Wagner, C. J. Allender, W. R. Easterday, V. Chenal-Francisque, P. Worsham, N. R. Thomson, J. Parkhill, L. E. Lindler, E. Carniel, and P. Keim. 2004. Microevolution and history of the plague bacillus, Yersinia pestis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101:17837-17842. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bierne, H., C. Sabet, N. Personnic, and P. Cossart. 2007. Internalins: a complex family of leucine-rich repeat-containing proteins in Listeria monocytogenes. Microbes Infect. 9:1156-1166. - PubMed
-
- Boerlin, P., J. Rocourt, F. Grimont, P. Grimont, C. Jacquet, and J. C. Piffaretti. 1992. Listeria ivanovii subsp. londoniensis subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 42:69-73. - PubMed
-
- Boerlin, P., J. Rocourt, and J. C. Piffaretti. 1991. Taxonomy of the genus Listeria by using multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 41:59-64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

