Angiotensin-(1-7) and low-dose angiotensin II infusion reverse salt-induced endothelial dysfunction via different mechanisms in rat middle cerebral arteries
- PMID: 20656887
- PMCID: PMC2957344
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00328.2010
Angiotensin-(1-7) and low-dose angiotensin II infusion reverse salt-induced endothelial dysfunction via different mechanisms in rat middle cerebral arteries
Abstract
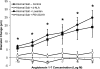
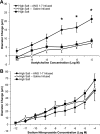
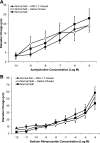
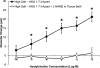
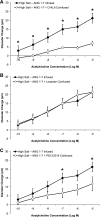
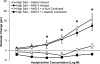
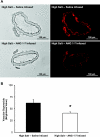
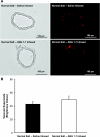
The goals of this study were to 1) determine the acute effect of ANG-(1-7) on vascular tone in isolated middle cerebral arteries (MCAs) from Sprague-Dawley rats fed a normal salt (NS; 0.4% NaCl) diet, 2) evaluate the ability of chronic intravenous infusion of ANG-(1-7) (4 ng·kg(-1)·min(-1)) for 3 days to restore endothelium-dependent dilation to acetylcholine (ACh) in rats fed a high-salt (HS; 4% NaCl) diet, and 3) determine whether the amelioration of endothelial dysfunction by ANG-(1-7) infusion in rats fed a HS diet is different from the protective effect of low-dose ANG II infusion in salt-fed rats. MCAs from rats fed a NS diet dilated in response to exogenous ANG-(1-7) (10(-10)-10(-5) M). Chronic ANG-(1-7) infusion significantly reduced vascular superoxide levels and restored the nitric oxide-dependent dilation to ACh (10(-10)-10(-5) M) that was lost in MCAs of rats fed a HS diet. Acute vasodilation to ANG-(1-7) and the restoration of ACh-induced dilation by chronic ANG-(1-7) infusion in rats fed a HS diet were blocked by the Mas receptor antagonist [D-ALA(7)]-ANG-(1-7) or the ANG II type 2 receptor antagonist PD-123319 and unaffected by ANG II type 1 receptor blockade with losartan. The restoration of ACh-induced dilation in MCAs of HS-fed rats by chronic intravenous infusion of ANG II (5 ng·kg(-1)·min(-1)) was blocked by losartan and unaffected by d-ALA. These findings demonstrate that circulating ANG-(1-7), working via the Mas receptor, restores endothelium-dependent vasodilation in cerebral resistance arteries of animals fed a HS diet via mechanisms distinct from those activated by low-dose ANG II infusion.
Figures
References
-
- Benter IF, Yousif MH, Dhaunsi GS, Kaur J, Chappell MC, Diz DI. Angiotensin-(1-7) prevents activation of NADPH oxidase and renal vascular dysfunction in diabetic hypertensive rats. Am J Nephrol 28: 25–33, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Boegehold MA. Flow-dependent arteriolar dilation in normotensive rats fed low- or high-salt diets. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 269: H1407–H1414, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Brosnihan KB, Li P, Tallant EA, Ferrario CM. Angiotensin-(1-7): a novel vasodilator of the coronary circulation. Biol Res 31: 227–234, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Campbell DJ, Kladis A, Duncan AM. Effects of converting enzyme inhibitors on angiotensin and bradykinin peptides. Hypertension 23: 439–449, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Canals M, Jenkins L, Kellett E, Milligan G. Up-regulation of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor by the MAS proto-oncogene is due to constitutive activation of Gq/G11 by MAS. J Biol Chem 281: 16757–16767, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

