Cardiomyocyte sulfonylurea receptor 2-KATP channel mediates cardioprotection and ST segment elevation
- PMID: 20656890
- PMCID: PMC2957346
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00084.2010
Cardiomyocyte sulfonylurea receptor 2-KATP channel mediates cardioprotection and ST segment elevation
Abstract
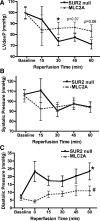
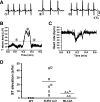
Sulfonylurea receptor-containing ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channels have been implicated in cardioprotection, but the cell type and constitution of channels responsible for this protection have not been clear. Mice deleted for the first nucleotide binding region of sulfonylurea receptor 2 (SUR2) are referred to as SUR2 null since they lack full-length SUR2 and glibenclamide-responsive K(ATP) channels in cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle. As previously reported, SUR2 null mice develop electrocardiographic changes of ST segment elevation that were shown to correlate with coronary artery vasospasm. Here we restored expression of the cardiomyocyte SUR2-K(ATP) channel in SUR2 null mice by generating transgenic mice with ventricular cardiomyocyte-restricted expression of SUR2A. Introduction of the cardiomyocyte SUR2A transgene into the SUR2 null background restored functional cardiac K(ATP) channels. Hearts isolated from rescued mice, referred to as MLC2A, had significantly reduced infarct size (27 ± 3% of area at risk) compared with SUR2 null mice (36 ± 3% of area at risk). Compared with SUR2 null hearts, MLC2A hearts exhibited significantly improved cardiac function during the postischemia reperfusion period primarily because of preservation of low diastolic pressures. Additionally, restoration of cardiac SUR2-K(ATP) channels significantly reduced the degree and frequency of ST segment elevation episodes in MLC2A mice. Therefore, cardioprotective mechanisms both dependent and independent of SUR2-K(ATP) channels contribute to cardiac function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spontaneous coronary vasospasm in KATP mutant mice arises from a smooth muscle-extrinsic process.Circ Res. 2006 Mar 17;98(5):682-9. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000207498.40005.e7. Epub 2006 Feb 2. Circ Res. 2006. PMID: 16456098
-
Mice lacking sulfonylurea receptor 2 (SUR2) ATP-sensitive potassium channels are resistant to acute cardiovascular stress.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007 Oct;43(4):445-54. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.07.058. Epub 2007 Aug 1. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17765261 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal KATP channels as a reservoir after myocardial ischemia: a role for SUR2 subunits.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Jan;300(1):H262-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00857.2010. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20971764 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfonylurea receptor 1 subunits of ATP-sensitive potassium channels and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2009 Feb;19(2):61-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2009.04.008. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2009. PMID: 19577714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac sarcolemmal K(ATP) channels: Latest twists in a questing tale!J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010 Jan;48(1):71-5. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.07.002. Epub 2009 Jul 14. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 19607836 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KATP Channels in the Cardiovascular System.Physiol Rev. 2016 Jan;96(1):177-252. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00003.2015. Physiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26660852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abcc9 is required for the transition to oxidative metabolism in the newborn heart.FASEB J. 2014 Jul;28(7):2804-15. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-244459. Epub 2014 Mar 19. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24648545 Free PMC article.
-
Cantú syndrome resulting from activating mutation in the KCNJ8 gene.Hum Mutat. 2014 Jul;35(7):809-13. doi: 10.1002/humu.22555. Epub 2014 May 6. Hum Mutat. 2014. PMID: 24700710 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin ameliorates rat myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through activation of peroxiredoxin II.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;175(16):3315-3332. doi: 10.1111/bph.14367. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29782637 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid signaling to membrane proteins: From second messengers to membrane domains and adapter-free endocytosis.J Gen Physiol. 2018 Feb 5;150(2):211-224. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201711875. Epub 2018 Jan 11. J Gen Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29326133 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brutsaert DL. Cardiac endothelial-myocardial signaling: its role in cardiac growth, contractile performance, and rhythmicity. Physiol Rev 83: 59–115, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Chutkow WA, Makielski JC, Nelson DJ, Burant CF, Fan Z. Alternative splicing of sur2 exon 17 regulates nucleotide sensitivity of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel. J Biol Chem 274: 13656–13665, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

