Cardiomyocyte sulfonylurea receptor 2-KATP channel mediates cardioprotection and ST segment elevation
- PMID: 20656890
- PMCID: PMC2957346
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00084.2010
Cardiomyocyte sulfonylurea receptor 2-KATP channel mediates cardioprotection and ST segment elevation
Abstract
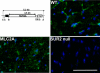
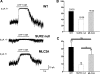
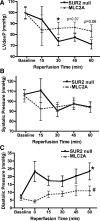
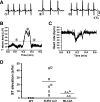
Sulfonylurea receptor-containing ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channels have been implicated in cardioprotection, but the cell type and constitution of channels responsible for this protection have not been clear. Mice deleted for the first nucleotide binding region of sulfonylurea receptor 2 (SUR2) are referred to as SUR2 null since they lack full-length SUR2 and glibenclamide-responsive K(ATP) channels in cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle. As previously reported, SUR2 null mice develop electrocardiographic changes of ST segment elevation that were shown to correlate with coronary artery vasospasm. Here we restored expression of the cardiomyocyte SUR2-K(ATP) channel in SUR2 null mice by generating transgenic mice with ventricular cardiomyocyte-restricted expression of SUR2A. Introduction of the cardiomyocyte SUR2A transgene into the SUR2 null background restored functional cardiac K(ATP) channels. Hearts isolated from rescued mice, referred to as MLC2A, had significantly reduced infarct size (27 ± 3% of area at risk) compared with SUR2 null mice (36 ± 3% of area at risk). Compared with SUR2 null hearts, MLC2A hearts exhibited significantly improved cardiac function during the postischemia reperfusion period primarily because of preservation of low diastolic pressures. Additionally, restoration of cardiac SUR2-K(ATP) channels significantly reduced the degree and frequency of ST segment elevation episodes in MLC2A mice. Therefore, cardioprotective mechanisms both dependent and independent of SUR2-K(ATP) channels contribute to cardiac function.
Figures

References
-
- Brutsaert DL. Cardiac endothelial-myocardial signaling: its role in cardiac growth, contractile performance, and rhythmicity. Physiol Rev 83: 59–115, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Chutkow WA, Makielski JC, Nelson DJ, Burant CF, Fan Z. Alternative splicing of sur2 exon 17 regulates nucleotide sensitivity of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel. J Biol Chem 274: 13656–13665, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

