The Aspergillus fumigatus cspA gene encoding a repeat-rich cell wall protein is important for normal conidial cell wall architecture and interaction with host cells
- PMID: 20656913
- PMCID: PMC2937338
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00126-10
The Aspergillus fumigatus cspA gene encoding a repeat-rich cell wall protein is important for normal conidial cell wall architecture and interaction with host cells
Abstract
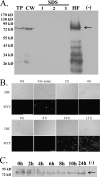
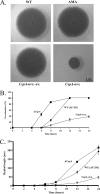
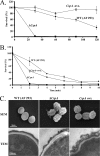
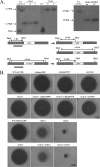
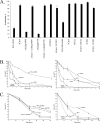
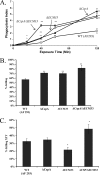
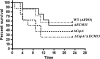
cspA (for cell surface protein A) encodes a repeat-rich glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell wall protein (CWP) in the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. The number of repeats in cspA varies among isolates, and this trait is used for typing closely related strains of A. fumigatus. We have previously shown that deletion of cspA is associated with rapid conidial germination and reduced adhesion of dormant conidia. Here we show that cspA can be extracted with hydrofluoric acid (HF) from the cell wall, suggesting that it is a GPI-anchored CWP. The cspA-encoded CWP is unmasked during conidial germination and is surface expressed during hyphal growth. Deletion of cspA results in weakening of the conidial cell wall, whereas its overexpression increases conidial resistance to cell wall-degrading enzymes and inhibits conidial germination. Double mutant analysis indicates that cspA functionally interacts with the cell wall protein-encoding genes ECM33 and GEL2. Deletion of cspA together with ECM33 or GEL2 results in strongly reduced conidial adhesion, increased disorganization of the conidial cell wall, and exposure of the underlying layers of chitin and beta-glucan. This is correlated with increasing susceptibility of the DeltacspA, DeltaECM33, and DeltacspA DeltaECM33 mutants to conidial phagocytosis and killing by human macrophages and hyphal damage induced by neutrophils. However, these strains did not exhibit altered virulence in mice with infected lungs. Collectively, these results suggest a role for cspA in maintaining the strength and integrity of the cell wall.
Figures
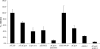


References
-
- Aimanianda V., Bayry J., Bozza S., Kniemeyer O., Perruccio K., Elluru S. R., Clavaud C., Paris S., Brakhage A. A., Kaveri S. V., Romani L., Latge J. P. 2009. Surface hydrophobin prevents immune recognition of airborne fungal spores. Nature 460:1117–1121 - PubMed
-
- Bainbridge B. W. 1971. Macromolecular composition and nuclear division during spore germination in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Gen. Microbiol. 66:319–325 - PubMed
-
- Balajee S. A., de Valk H. A., Lasker B. A., Meis J. F., Klaassen C. H. 2008. Utility of a microsatellite assay for identifying clonally related outbreak isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Microbiol. Methods 73:252–256 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

