Noninterleaved velocity encodings for improved temporal and spatial resolution in phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 20657227
- PMCID: PMC3071154
- DOI: 10.1097/RCT.0b013e3181d564e8
Noninterleaved velocity encodings for improved temporal and spatial resolution in phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
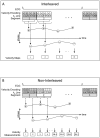
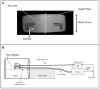
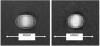
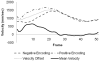
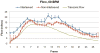
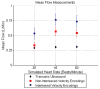
A segmented k-space acquisition technique using noninterleaved velocity encodings is presented to reduce spatial and temporal blur in phase-contrast cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. A translating phantom with pulsatile flow was used to simulate imaging of coronary arteries on a 1.5-T GE Echospeed scanner, using both interleaved and noninterleaved velocity encodings. The results demonstrate that the use of noninterleaved velocity encodings reduces spatial and temporal blur by improving the temporal resolution.
Figures



References
-
- Hundley WG, Lange RA, Clarke GD, et al. Assessment of coronary arterial flow and flow reserve in humans with magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation. 1996 April 15;93(8):1502–8. - PubMed
-
- Davis CP, Liu PF, Hauser M, Gohde SC, von Schulthess GK, Debatin JF. Coronary flow and coronary flow reserve measurements in humans with breath-held magnetic resonance phase contrast velocity mapping. Magn Reson Med. 1997 April;37(4):537–44. - PubMed
-
- Hofman MB, Wickline SA, Lorenz CH. Quantification of in-plane motion of the coronary arteries during the cardiac cycle: implications for acquisition window duration for MR flow quantification. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1998 May;8(3):568–76. - PubMed
-
- Moran PR. A flow velocity zeugmatographic interlace for NMR imaging in humans. Magn Reson Imaging. 1982;1(4):197–203. - PubMed
-
- Haacke EM, Bearden FH, Clayton JR, Linga NR. Reduction of MR imaging time by the hybrid fast-scan technique. Radiology. 1986 February;158(2):521–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

