Increased rat neonatal activity influences adult cytokine levels and relative muscle mass
- PMID: 20657345
- PMCID: PMC4242013
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181f2e836
Increased rat neonatal activity influences adult cytokine levels and relative muscle mass
Abstract
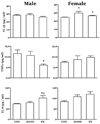
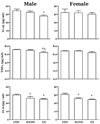
Little is known about the effect of physical activity in early life on subsequent growth and regulation of inflammation. We previously reported that exposure of muscles in growing rats to IL-6 results in decreased muscle growth apparently because of a state of resistance to growth factors such IGF-I and that running exercise could ameliorate this growth defect. Herein, we hypothesized that increased activity, for a brief period during neonatal life, would pattern the adult rat toward a less inflammatory phenotype. Neonatal rats were induced to move about their cage for brief periods from d 5 to d 15 postpartum. Additional groups were undisturbed controls (CONs) and handled (HAND). Subgroups of rats were sampled at the age of 30 and 65 d. Relative to CON and HAND groups, the neonatal exercise (EX) group demonstrated a decrease in circulating levels of TNFα, IL-6, and IL-1β in adulthood, primarily in male rats. In addition, adult male EX rats had lower body mass and increased skeletal muscle mass suggesting a leaner phenotype. The results of this study suggest that moderate increases in activity early in life can influence the adult toward a more healthy phenotype with regard to inflammatory mediators and relative muscle mass.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beneficial alterations in body composition, physical performance, oxidative stress, inflammatory markers, and adipocytokines induced by long-term high-intensity interval training in an aged rat model.Exp Gerontol. 2018 Nov;113:150-162. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Exp Gerontol. 2018. PMID: 30308288
-
The effect of acute and prolonged endurance exercise on transforming growth factor-beta1 generation in rat skeletal and heart muscle.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;60(4):157-62. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20065510
-
Surgical manipulation, but not moderate exercise, is associated with increased cytokine mRNA expression in the rat soleus muscle.Acta Physiol Scand. 2002 Jul;175(3):219-26. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-201X.2002.00990.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2002. PMID: 12100361
-
Chronic exercise decreases cytokine production in healthy rat skeletal muscle.Cell Biochem Funct. 2009 Oct;27(7):458-61. doi: 10.1002/cbf.1594. Cell Biochem Funct. 2009. PMID: 19681095
-
Cytokine responses to physical activity, with particular reference to IL-6: sources, actions, and clinical implications.Crit Rev Immunol. 2002;22(3):165-82. Crit Rev Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12498381 Review.
Cited by
-
Body composition and neuromotor development in the year after NICU discharge in premature infants.Pediatr Res. 2020 Sep;88(3):459-465. doi: 10.1038/s41390-020-0756-2. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Pediatr Res. 2020. PMID: 31926484 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Links between thermoregulation and aging in endotherms and ectotherms.Temperature (Austin). 2014 Dec 20;2(1):73-85. doi: 10.4161/23328940.2014.989793. eCollection 2015 Jan-Mar. Temperature (Austin). 2014. PMID: 27226994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth inhibition and compensation in response to neonatal hypoxia in rats.Pediatr Res. 2013 Aug;74(2):111-20. doi: 10.1038/pr.2013.80. Epub 2013 May 22. Pediatr Res. 2013. PMID: 23842077 Free PMC article.
-
Low-cost, open-source, variable speed and incline treadmill for studying impacts of neonatal locomotion.HardwareX. 2020 Jan 21;7:e00097. doi: 10.1016/j.ohx.2020.e00097. eCollection 2020 Apr. HardwareX. 2020. PMID: 35495209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bechtold S, Alberer M, Arenz T, Putzker S, Filipiak-Pittroff B, Schwarz HP, Koletzko S. Reduced muscle mass and bone size in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010;16:216–225. - PubMed
-
- Bechtold S, Dalla PR, Schwarz HP, Simon D. Effects of growth hormone treatment in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: bone and body composition. Horm Res. 2009;72:60–64. - PubMed
-
- Moser C, Tirakitsoontorn P, Nussbaum E, Newcomb R, Cooper DM. Muscle Size and Cardiorespiratory Response to Exercise in Cystic Fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:1823–1827. - PubMed
-
- Vahlkvist S, Pedersen S. Fitness, daily activity and body composition in children with newly diagnosed, untreated asthma. Allergy. 2009;64:1649–1655. - PubMed

