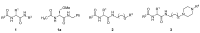Solid-phase synthetic route to multiple derivatives of a fundamental peptide unit
- PMID: 20657403
- PMCID: PMC6257617
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15074961
Solid-phase synthetic route to multiple derivatives of a fundamental peptide unit
Abstract
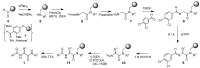
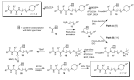
Amino acids are Nature's combinatorial building blocks. When substituted on both the amino and carboxyl sides they become the basic scaffold present in all peptides and proteins. We report a solid-phase synthetic route to large combinatorial variations of this fundamental scaffold, extending the variety of substituted biomimetic molecules available to successfully implement the Distributed Drug Discovery (D3) project. In a single solid-phase sequence, compatible with basic amine substituents, three-point variation is performed at the amino acid a-carbon and the amino and carboxyl functionalities.
Figures
References
-
- Scott W.L., Alsina J., Audu C.O., Babaev E., Cook L., Dage J.L., Goodwin L.A., Martynow J.G., Matosiuk D., Royo M., Smith J.G., Strong A.T., Wickizer K., Woerly E.M., Zhou Z., O’Donnell M.J. Distributed drug discovery, part 2: Global rehearsal of alkylating agents for the synthesis of resin-bound unnatural amino acids and virtual D3 catalog construction. J. Comb. Chem. 2009;11:14–33. doi: 10.1021/cc800184v. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scott W.L., Audu C.O., Dage J.L., Goodwin L.A., Martynow J.G., Platt L.K, Smith J.G., Strong A.T., Wickizer K., Woerly E.M., O’Donnell M.J. Distributed drug discovery, part 3: Using D3 methodology to synthesize analogs of an anti-melanoma compound. J. Comb. Chem. 2009;11:34–43. doi: 10.1021/cc800185z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- O'Donnell M.J., Zhou C., Scott W.L. Solid-phase unnatural peptide synthesis (UPS) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996;118:6070–6071. doi: 10.1021/ja9601245. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources