Design, synthesis and structure-activity studies of rhodanine derivatives as HIV-1 integrase inhibitors
- PMID: 20657419
- PMCID: PMC6264390
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15063958
Design, synthesis and structure-activity studies of rhodanine derivatives as HIV-1 integrase inhibitors
Abstract
Raltegravir was the first HIV-1 integrase inhibitor that gained FDA approval for use in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Because of the emergence of IN inhibitor-resistant viral strains, there is a need to identify innovative second-generation IN inhibitors. Previously, we identified 2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone (rhodanine)-containing compounds as IN inhibitors. Herein, we report the design, synthesis and docking studies of a series of novel rhodanine derivatives as IN inhibitors. All these compounds were further tested against human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) to determine their selectivity. Two compounds showed significant cytotoxicity in a panel of human cancer cell lines. Taken together, our results show that rhodanines are a promising class of compounds for developing drugs with antiviral and anticancer properties.
Figures
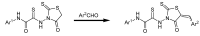
References
-
- Vandegraaff N., Engelman A. Molecular mechanisms of HIV integration and therapeutic intervention. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2007;9:1–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

