Synthesis and bioactivity of N-benzoyl-N'-[5-(2'-substituted phenyl)-2-furoyl] semicarbazide derivatives
- PMID: 20657440
- PMCID: PMC6257640
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15064267
Synthesis and bioactivity of N-benzoyl-N'-[5-(2'-substituted phenyl)-2-furoyl] semicarbazide derivatives
Abstract
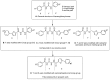
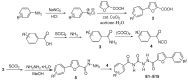
In order to find novel chitin synthesis inhibitors (CSIs) with good activity, benzoylphenylurea, a typical kind of CSIs, was chosen as the lead compound and 15 novel derivatives containing furan moieties were designed by converting the urea linkage of benzoylphenylureas into a semicarbazide and changing the aniline part into furoyl groups. The title compounds were synthesized by the reaction of substituted benzoyl isocyanates with 5-(substituted phenyl)-2-furoyl hydrazine, and the structures were confirmed by IR, (1)H-NMR, elemental analysis and single crystal X-ray diffraction analyses (compound E2). The bioassay results indicated that the title compounds exhibit good insecticidal activity, especially towards Plutella xylostella L., but had lower fungicidal activity. Inspiringly, the title compounds possessed obvious anticancer activity against human promyelocytic leukemic cell line (HL-60), and some of the title compounds also had activity against human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (Bel-7402), human gastric carcinoma cell line (BGC-823), and human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (KB). The results indicated that the linkage in the lead compounds was important to the bioactivity and spectra. The modification on the urea linkage is an effective strategy to discover new pesticide and drug candidates.
Figures
References
-
- Oberlander H., Silhacek D.L. New Perspectives on the Mode of Action of Benzoylphenyl Urea Insecticides. In: Ishaaya I., Degheele D., editors. Insecticides with Novel Modes of Action: Mechanism and Application. 1st ed. Springer-Verlag; Berlin, Germany: 1998. pp. 92–105.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources