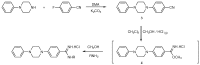
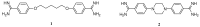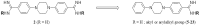Bisbenzamidines as antifungal agents. are both amidine functions required to observe an anti-Pneumocystis carinii activity?
- PMID: 20657441
- PMCID: PMC6257595
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15064283
Bisbenzamidines as antifungal agents. are both amidine functions required to observe an anti-Pneumocystis carinii activity?
Abstract
A library of 19 novel 4-(4-phenylpiperazine-1-yl)benzamidines has been synthesized and evaluated in vitro against Pneumocystis carinii. Among these compounds, N-ethyl- and N-hexyl-4-(4-phenylpiperazine-1-yl)benzamidines emerged as the most promising compounds, with inhibition percentages at 10.0 microg/mL of 87% and 96%, respectively. Those compounds remained active at 0.1 microg/mL.
Figures
References
-
- Donkor I.O., Queener S.F., Dalton J.T. Pentamidine congeners: DNA binding affinity and anti-Pneumocystis carinii activity of butamidine analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996;6:1967–1970. doi: 10.1016/0960-894X(96)00353-8. - DOI
-
- Delia T.J., Nagarajan A., Queener S.F., Bartlett M.S. Ring-based analogues of pentamidine versus P. carinii pneumonia in culture. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1996;6:2367–2370. doi: 10.1016/0960-894X(96)00427-1. - DOI
-
- Huang T.L., Vanden Eynde J.J., Mayence A., Collins M.S., Cushion M.T., Rattendi D., Londono I., Mazumder L., Bacchi C.J., Yarlett N. Synthesis and SAR of alcanediamide-linked bisbenzamidines with anti-trypanosomal and anti-pneumocystis activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009;19:5884–5886. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.08.073. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources