Characterization of aromatase binding agents from the dichloromethane extract of Corydalis yanhusuo using ultrafiltration and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 20657498
- PMCID: PMC6263280
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15053556
Characterization of aromatase binding agents from the dichloromethane extract of Corydalis yanhusuo using ultrafiltration and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
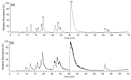
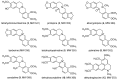
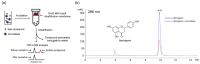
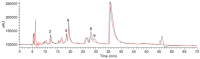
Aromatase represents an important target for the treatment of hormone-dependent breast cancer. In the present study, nine alkaloids from the dichloromethane extract of Corydalis yanhusuo were identified by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and tested for their aromatase binding activities using an ultrafiltration LC-MS method by investigating the differences of peak areas of compounds before and after incubations with aromatase. It was demonstrated that the quaternary protoberberine alkaloids and the tertiary protoberberine alkaloids exhibited potent aromatase binding activities. The quaternary ammonium group and the methyl group at C-13 position of tertiary protoberberine alkaloids might be necessary for the activity. The findings should provide guidance for the discovery of potential aromatase inhibitors from natural products.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HPLC-MS analysis of ethanol extract of Corydalis yanhusuo and simultaneous determination of eight protoberberine quaternary alkaloids by HPLC-DAD.J Chromatogr Sci. 2010 Jul;48(6):441-4. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/48.6.441. J Chromatogr Sci. 2010. PMID: 20822657
-
Qualitative and quantitative determination of ten alkaloids in traditional Chinese medicine Corydalis yanhusuo W.T. Wang by LC-MS/MS and LC-DAD.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007 Oct 18;45(2):219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2007.06.009. Epub 2007 Jun 14. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007. PMID: 17640842
-
Development and Validation of a HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Fourteen Alkaloids in Mouse Plasma after Oral Administration of the Extract of Corydalis yanhusuo Tuber: Application to Pharmacokinetic Study.Molecules. 2018 Mar 21;23(4):714. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040714. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29561801 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic screening and characterization of tertiary and quaternary alkaloids from corydalis yanhusuo W.T. Wang using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Talanta. 2009 Apr 30;78(2):513-22. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2008.12.002. Epub 2008 Dec 6. Talanta. 2009. PMID: 19203617
-
The Analgesic Properties of Corydalis yanhusuo.Molecules. 2021 Dec 10;26(24):7498. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247498. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent progress on the traditional Chinese medicines that regulate the blood.J Food Drug Anal. 2016 Apr;24(2):221-238. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2015.10.009. Epub 2016 Jan 5. J Food Drug Anal. 2016. PMID: 28911575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-proliferative activity of Fumaria vaillantii extracts on different cancer cell lines.Res Pharm Sci. 2016 Mar-Apr;11(2):152-9. Res Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27168755 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of α-Amylase Inhibitors from Kadsura longipedunculata Using a High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography Target Guided by Centrifugal Ultrafiltration with LC-MS.Molecules. 2016 Sep 7;21(9):1190. doi: 10.3390/molecules21091190. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27617987 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Selected Isoquinoline Alkaloids from Mahonia Aquifolia; Meconopsis Cambrica; Corydalis Lutea; Dicentra Spectabilis; Fumaria Officinalis; Macleaya Cordata Extracts by HPLC-DAD and Comparison of Their Cytotoxic Activity.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Oct 2;11(10):575. doi: 10.3390/toxins11100575. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31581717 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of wine and vinegar processing of Rhizoma Corydalis on the tissue distribution of tetrahydropalmatine, protopine and dehydrocorydaline in rats.Molecules. 2012 Jan 18;17(1):951-70. doi: 10.3390/molecules17010951. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22258341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bulun S.E., Lin Z., Imir G., Amin S., Demura M., Yilmaz B., Martin R., Utsunomiya H., Thung S., Gurates B., Tamura M., Langoi D., Deb S. Regulation of aromatase expression in estrogen-responsive breast and uterine disease: from bench to treatment. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005;57:359–383. doi: 10.1124/pr.57.3.6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fisher B., Costantino J.P., Wickerham D.L., Redmond C.K., Kavanah M., Cronin W.M., Vogel V., Robidoux A., Dimitrov N., Atkins J., Daly M., Wieand S., Tan-Chiu E., Ford L., Wolmark N. Tamoxifen for prevention of breast caner: Report of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998;90:1371–1388. doi: 10.1093/jnci/90.18.1371. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

