Human RING finger protein ZNF645 is a novel testis-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase
- PMID: 20657603
- PMCID: PMC3739317
- DOI: 10.1038/aja.2010.54
Human RING finger protein ZNF645 is a novel testis-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase
Abstract
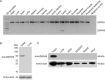
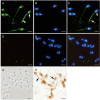
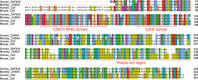
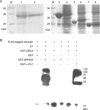
A large number of testis-specific genes are involved in the complex process of mammalian spermatogenesis. Identification of these genes and their roles is important for understanding the mechanisms underlying spermatogenesis. Here we report on a novel human RING finger protein, ZNF645, which contains a C3HC4 RING finger domain, a C2H2 zinc-finger domain, and a proline-rich region, indicating that it has a structure similar to that of the c-Cbl-like protein Hakai. ZNF645 was exclusively expressed in normal human testicular tissue. Immunohistochemical analysis confirmed that ZNF645 protein was present in spermatocytes, round and elongated spermatids, and Leydig cells. Immunofluorescence staining of mature sperms further showed that the ZNF645 protein was localized over the postacrosomal perinuclear theca region and the entire length of sperm tail. An in vitro ubiquitination assay indicated that the RING finger domain of the ZNF645 protein had E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Therefore, we suggest that ZNF645 might act as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase and play a role in human sperm production and quality control.
Figures



References
-
- Russell LD, Ettlin RA, Sinha HAP, Clegg ED.Mammalian spermatogenesisIn: Russell LD, Ettlin RA, Sinha HAP, Clegg ED, editors. Histological and Histopathological Evaluation of the Testis. St. Louis: Cache River Press; 1990pp1–40.
-
- Nass SJ, Strauss JF. Strategies to facilitate the development of new contraceptives. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:885–90. - PubMed
-
- Borden KLB. RING domains: master builders of molecular scaffolds. J Mol Biol. 2000;295:1103–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

