Identification of two aberrant transcripts derived from a hybridoma with amplification of functional immunoglobulin variable genes
- PMID: 20657605
- PMCID: PMC4002682
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2010.33
Identification of two aberrant transcripts derived from a hybridoma with amplification of functional immunoglobulin variable genes
Abstract
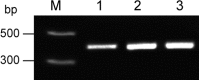
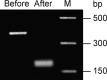
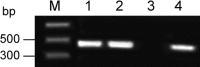
Murine monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are widely used but have limitations if administered in humans. The use of chimeric or humanized mAbs can reduce immunogenicity. The first step in producing such mAbs is to clone murine variable genes from a hybridoma, but it is possible to amplify both functional and aberrant variable genes, as they coexist in the hybridoma. During the development of a murine-human chimeric antibody, we have cloned from a hybridoma the functional heavy chain variable region (V(H)) and light chain variable region (V(L)) genes of a mAb that blocks the binding of anthrax lethal factor to protective antigen. In this study, we report the detection of two aberrant transcripts from a hybridoma produced using myeloma cell line OUR-1, the development of a method to distinguish between the functional and abundant aberrant V(L) transcripts, and the origins of these aberrant genes. The aberrant V(L) gene is derived from OUR-1 cells, while the aberrant V(H) gene might derive from antibody repertoires in B cells or from gene rearrangement in the hybridoma cells. The aberrant V(H) and V(L) genes in this study may facilitate discrimination between the functional and aberrant variable genes from hybridoma cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PCR amplification of the functional immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene from a hybridoma in the presence of two aberrant transcripts.J Immunol Methods. 2008 Jul 31;336(2):246-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2008.04.014. Epub 2008 May 16. J Immunol Methods. 2008. PMID: 18538340
-
A simple approach to identify functional antibody variable genes in murine hybridoma cells that coexpress aberrant kappa light transcripts by restriction enzyme digestion.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2021 Dec;39(4):287-295. doi: 10.12932/AP-031218-0452. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2021. PMID: 31175718
-
Identification and verification of hybridoma-derived monoclonal antibody variable region sequences using recombinant DNA technology and mass spectrometry.Mol Immunol. 2017 Oct;90:287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28865256
-
Comparison of two functional kappa light-chain transcripts amplified from a hybridoma.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2013 May-Jun;60(3):289-97. doi: 10.1002/bab.1080. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23631518
-
Hybridoma technology: is it still useful?Curr Res Immunol. 2021 Mar 22;2:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.crimmu.2021.03.002. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35492397 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Variable Region Genes and Discovery of Key Recognition Sites in the Complementarity Determining Regions of the Anti-Thiacloprid Monoclonal Antibody.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 18;21(18):6857. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186857. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32962080 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired proliferation and migration of HUVEC and melanoma cells by human anti-FGF2 mAbs derived from a murine hybridoma by guided selection.Bioengineered. 2023 Dec;14(1):2252667. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2023.2252667. Bioengineered. 2023. PMID: 37661761 Free PMC article.
-
When monoclonal antibodies are not monospecific: Hybridomas frequently express additional functional variable regions.MAbs. 2018 May/Jun;10(4):539-546. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1445456. Epub 2018 Mar 29. MAbs. 2018. PMID: 29485921 Free PMC article.
-
High-volume hybridoma sequencing on the NeuroMabSeq platform enables efficient generation of recombinant monoclonal antibodies and scFvs for neuroscience research.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 27;13(1):16200. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43233-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37758930 Free PMC article.
-
A simplified workflow for monoclonal antibody sequencing.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 24;14(6):e0218717. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218717. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31233538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuenen B, Witteveen PO, Ruijter R, Giaccone G, Dontabhaktuni A, Fox F, et al. A phase I pharmacologic study of necitumumab (IMC-11F8), a fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody directed against EGFR in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:1915–1923. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

