R5 clade C SHIV strains with tier 1 or 2 neutralization sensitivity: tools to dissect env evolution and to develop AIDS vaccines in primate models
- PMID: 20657739
- PMCID: PMC2908149
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011689
R5 clade C SHIV strains with tier 1 or 2 neutralization sensitivity: tools to dissect env evolution and to develop AIDS vaccines in primate models
Abstract
Background: HIV-1 clade C (HIV-C) predominates worldwide, and anti-HIV-C vaccines are urgently needed. Neutralizing antibody (nAb) responses are considered important but have proved difficult to elicit. Although some current immunogens elicit antibodies that neutralize highly neutralization-sensitive (tier 1) HIV strains, most circulating HIVs exhibiting a less sensitive (tier 2) phenotype are not neutralized. Thus, both tier 1 and 2 viruses are needed for vaccine discovery in nonhuman primate models.
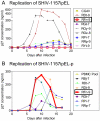
Methodology/principal findings: We constructed a tier 1 simian-human immunodeficiency virus, SHIV-1157ipEL, by inserting an "early," recently transmitted HIV-C env into the SHIV-1157ipd3N4 backbone [1] encoding a "late" form of the same env, which had evolved in a SHIV-infected rhesus monkey (RM) with AIDS. SHIV-1157ipEL was rapidly passaged to yield SHIV-1157ipEL-p, which remained exclusively R5-tropic and had a tier 1 phenotype, in contrast to "late" SHIV-1157ipd3N4 (tier 2). After 5 weekly low-dose intrarectal exposures, SHIV-1157ipEL-p systemically infected 16 out of 17 RM with high peak viral RNA loads and depleted gut CD4+ T cells. SHIV-1157ipEL-p and SHIV-1157ipd3N4 env genes diverge mostly in V1/V2. Molecular modeling revealed a possible mechanism for the increased neutralization resistance of SHIV-1157ipd3N4 Env: V2 loops hindering access to the CD4 binding site, shown experimentally with nAb b12. Similar mutations have been linked to decreased neutralization sensitivity in HIV-C strains isolated from humans over time, indicating parallel HIV-C Env evolution in humans and RM.
Conclusions/significance: SHIV-1157ipEL-p, the first tier 1 R5 clade C SHIV, and SHIV-1157ipd3N4, its tier 2 counterpart, represent biologically relevant tools for anti-HIV-C vaccine development in primates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Rerks-Ngarm S, Pitisuttithum P, Nitayaphan S, Kaewkungwal J, Chiu J, et al. Vaccination with ALVAC and AIDSVAX to prevent HIV-1 infection in Thailand. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2209–2220. - PubMed
-
- Walker BD, Burton DR. Toward an AIDS vaccine. Science. 2008;320:760–764. - PubMed
-
- Burke B, Barnett SW. Broadening our view of protective antibody responses against HIV. Curr HIV Res. 2007;5:625–641. - PubMed
-
- Pope M, Haase AT. Transmission, acute HIV-1 infection and the quest for strategies to prevent infection. Nat Med. 2003;9:847–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

