CD4+ and CD8+ T cells can act separately in tumour rejection after immunization with murine pneumotropic virus chimeric Her2/neu virus-like particles
- PMID: 20657846
- PMCID: PMC2906518
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011580
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells can act separately in tumour rejection after immunization with murine pneumotropic virus chimeric Her2/neu virus-like particles
Abstract
Background: Immunization with murine pneumotropic virus virus-like particles carrying Her2/neu (Her2MPtVLPs) prevents tumour outgrowth in mice when given prophylactically, and therapeutically if combined with the adjuvant CpG. We investigated which components of the immune system are involved in tumour rejection, and whether long-term immunological memory can be obtained.
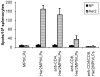
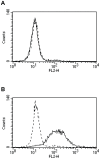
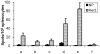
Methodology and results: During the effector phase in BALB/c mice, only depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ in combination, with or without NK cells, completely abrogated tumour protection. Depletion of single CD4+, CD8+ or NK cell populations only had minor effects. During the immunization/induction phase, combined depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ cells abolished protection, while depletion of each individual subset had no or negligible effect. When tumour rejection was studied in knock-out mice with a C57Bl/6 background, protection was lost in CD4-/-CD8-/- and CD4-/-, but not in CD8-/- mice. In contrast, when normal C57Bl/6 mice were depleted of different cell types, protection was lost irrespective of whether only CD4+, only CD8+, or CD4+ and CD8+ cells in combination were eradicated. No anti-Her2/neu antibodies were detected but a Her2/neu-specific IFNgamma response was seen. Studies of long-term memory showed that BALB/c mice could be protected against tumour development when immunized together with CpG as long as ten weeks before challenge.
Conclusion: Her2MPtVLP immunization is efficient in stimulating several compartments of the immune system, and induces an efficient immune response including long-term memory. In addition, when depleting mice of isolated cellular compartments, tumour protection is not as efficiently abolished as when depleting several immune compartments together.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting of the non-mutated tumor antigen HER2/neu to mature dendritic cells induces an integrated immune response that protects against breast cancer in mice.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 7;14(2):R39. doi: 10.1186/bcr3135. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22397502 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-dependent natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity engendered by a kinase-inactive human HER2 adenovirus-based vaccination mediates resistance to breast tumors.Cancer Res. 2010 Oct 1;70(19):7431-41. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0493. Epub 2010 Sep 7. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20823150
-
Murine pneumotropic virus chimeric Her2/neu virus-like particles as prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines against Her2/neu expressing tumors.Int J Cancer. 2009 Jan 1;124(1):150-6. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23920. Int J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 18839427
-
Insights into the mechanism of anti-tumor immunity in mice vaccinated with the human HER2/neu extracellular domain plus anti-HER2/neu IgG3-(IL-2) or anti-HER2/neu IgG3-(GM-CSF) fusion protein.Vaccine. 2005 Sep 15;23(39):4793-803. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.04.041. Vaccine. 2005. PMID: 15967544
-
NK1.1+ cells are important for the development of protective immunity against MHC I-deficient, HPV16-associated tumours.Oncol Rep. 2011 Jan;25(1):281-8. Oncol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21109988
Cited by
-
DNA vaccine that targets hemagglutinin to MHC class II molecules rapidly induces antibody-mediated protection against influenza.J Immunol. 2013 Sep 15;191(6):3221-31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300504. Epub 2013 Aug 16. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23956431 Free PMC article.
-
A simple, clinically relevant therapeutic vaccine shows long-term protection in an aggressive, delayed-treatment B lymphoma model.JCI Insight. 2017 Nov 16;2(22):e92522. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.92522. eCollection 2017 Nov 16. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 29202455 Free PMC article.
-
The specificity of targeted vaccines for APC surface molecules influences the immune response phenotype.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 11;8(11):e80008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080008. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244595 Free PMC article.
-
Murine polyomavirus virus-like particles carrying full-length human PSA protect BALB/c mice from outgrowth of a PSA expressing tumor.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023828. Epub 2011 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21858228 Free PMC article.
-
Microenvironment-derived ADAM28 prevents cancer dissemination.Oncotarget. 2018 Dec 14;9(98):37185-37199. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26449. eCollection 2018 Dec 14. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30647853 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bargmann C, Hung M, Weinberg R. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986;319:226–230. - PubMed
-
- Pupa S, Ménard S, Andreola S, Colnaghi M. Antibody response against the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in breast carcinoma patients. Cancer Res. 1993;53:5864–5866. - PubMed
-
- Disis M, Knutson K, Schiffman K, Rinn K, McNeel D. Pre-existent immunity to the HER-2/neu oncogenic protein in patients with HER-2/neu overexpressing breast and ovarian cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2000;62:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Salunke D, Caspar D, Garcea R. Self-assembly of purified polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. Cell. 1986;46:895–904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

