A two-component nonlinear mixed effects model for longitudinal data, with application to gastric emptying studies
- PMID: 20658551
- PMCID: PMC3608145
- DOI: 10.1002/sim.3956
A two-component nonlinear mixed effects model for longitudinal data, with application to gastric emptying studies
Abstract
Gastric emptying studies are of great interest in human and veterinary medical research to evaluate effects of medications or diets for promoting gastrointestinal motility and to examine unintended side-effects of new or existing medications, diets, or procedures. Summarizing gastric emptying data is important to allow easier comparison between treatments or groups of subjects and comparisons of results among studies. The standard method for assessing gastric emptying is by using scintigraphy and summarizing the nonlinear emptying of the radioisotope. A popular model for fitting gastric emptying data is the power exponential model. This model can only describes a globally decreasing pattern and thus has the limitation of poorly describing localized intragastric events that can occur during emptying. Hence, we develop a new model for gastric emptying studies to improve population and individual inferences using a mixture of nonlinear mixed effects models. One mixture component is based on a power exponential model which captures globally decreasing patterns. The other is based on a locally extended power exponential model which captures both local bumping and rapid decay. We refer to this mixture model as a two-component nonlinear mixed effects model. The parameters in our model have clear graphical interpretations that provide a more accurate representation and summary of the curves of gastric emptying pattern. Two methods are developed to fit our proposed model: one is the mixture of an Expectation Maximization algorithm and a global two-stage method and the other is the mixture of an Expectation Maximization algorithm and the Monte Carlo Expectation Maximization algorithm. We compare our methods using simulation, showing that the two approaches are comparable to one another. For estimating the variance and covariance matrix, the second approach appears approximately more efficient and is also numerically more stable in some cases. Our new model and approaches are applicable for assessing gastric emptying in human and veterinary medical research and in many other biomedical fields such as pharmacokinetics, toxicokinetics, and physiological research. An example of gastric emptying data from equine medicine is used to demonstrate the advantage of our approaches.
Copyright (c) 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
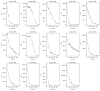
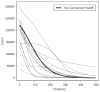
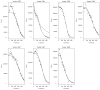
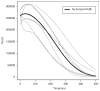
Similar articles
-
A gamma variate model that includes stretched exponential is a better fit for gastric emptying data from mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Aug 1;309(3):G162-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00280.2014. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26045615 Free PMC article.
-
Structural identifiability analysis of pharmacokinetic models using DAISY: semi-mechanistic gastric emptying models for 13C-octanoic acid.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2011 Apr;38(2):279-92. doi: 10.1007/s10928-011-9193-5. Epub 2011 Feb 24. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2011. PMID: 21347679
-
Measurement of gastric emptying by the 13C-octanoate breath test--rationalization with scintigraphy.Physiol Meas. 2006 Mar;27(3):279-89. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/27/3/006. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Physiol Meas. 2006. PMID: 16462014
-
Radionuclide gastroesophageal motor studies.J Nucl Med. 2004 Jun;45(6):1004-28. J Nucl Med. 2004. PMID: 15181137 Review.
-
Gastric Emptying in the Elderly.Clin Geriatr Med. 2015 Aug;31(3):339-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 May 11. Clin Geriatr Med. 2015. PMID: 26195094 Review.
Cited by
-
A Simple, Realistic Stochastic Model of Gastric Emptying.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 8;11(4):e0153297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153297. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27057750 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of gastric emptying with magnetic resonance imaging in healthy volunteers: A systematic review.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022 Dec;34(12):e14371. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14371. Epub 2022 Mar 27. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022. PMID: 35340100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meyer JH, Ohashi H, Jehn D, Thomson JB. Size of liver particles emptied from the human stomach. Gastroenterology. 1981;80:1489–1496. - PubMed
-
- Camilleri M, Colemont LJ, Phillips SF, Brown ML, Thomforde GM, Chapman N, Zinsmeister R. Human gastric emptying and colonic filling of solids characterized by a new method. American Journal of Physiology Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 1989;257:G284–G290. - PubMed
-
- Akkermans LMA, Van Isselt JW. Gastric motility and emptying studies with radionuclides in research and clinical settings. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 1994;39:95S–96S. - PubMed
-
- Debreceni A, Abdel-Salam OME, Figler M, Juricskay I, Szolcsanyi J, Mozsik G. Capsicin increases gastric emptying rate in health human subjects measured by 13C-labeled octanoic acid breath test. Journal of Physiology. 1999;93:455–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
