Mechanisms of resurgence of an extinguished instrumental behavior
- PMID: 20658865
- PMCID: PMC3113596
- DOI: 10.1037/a0017365
Mechanisms of resurgence of an extinguished instrumental behavior
Abstract
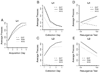
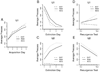
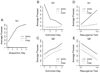
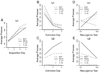
Four experiments examined "resurgence" of an instrumental behavior after extinction. All experiments involved three phases in which rats were (1) trained to press one lever for food reward, (2) trained to press a second lever while the first leverpress was extinguished, and (3) tested under conditions in which neither leverpress was rewarded. In each experiment, the first leverpress recovered (resurged) in Phase 3, when the second leverpress was extinguished. The results demonstrated that resurgence occurred when the schedules of reinforcement employed in Phases 1 and 2 yielded either an upshift, downshift, or no change in the rate of reward delivery between those phases. They also demonstrated that initial training on the first lever was required to observe a robust increase in pressing at test (resurgence is thus an associative effect). Resurgence was shown to occur over a wide variety of schedules of reinforcement in Phase 2 (including ratio, interval, and leverpress-independent schedules). Finally, the results do not support the view that resurgence occurs because response competition suppresses leverpressing of the first lever during extinction. Overall, they are consistent with the view that resurgence is a renewal effect in which extinction of an instrumental behavior is specific to the context provided by rewarded leverpressing during the extinction phase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of thinning the rate at which the alternative behavior is reinforced on resurgence of an extinguished instrumental response.J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2012 Jul;38(3):279-91. doi: 10.1037/a0028853. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 2012. PMID: 22823421 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of reinforcer distribution during response elimination on resurgence of an instrumental behavior.J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2015 Apr;41(2):179-92. doi: 10.1037/xan0000061. Epub 2015 Mar 23. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2015. PMID: 25798714 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that encourage generalization from extinction to test reduce resurgence of an extinguished operant response.J Exp Anal Behav. 2018 Jul;110(1):11-23. doi: 10.1002/jeab.446. Epub 2018 Jun 17. J Exp Anal Behav. 2018. PMID: 29911341 Free PMC article.
-
Resurgence as Choice.Behav Processes. 2017 Aug;141(Pt 1):100-127. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Behav Processes. 2017. PMID: 27794452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On defining resurgence.Behav Processes. 2017 Aug;141(Pt 1):85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2017.04.018. Epub 2017 May 6. Behav Processes. 2017. PMID: 28487201 Review.
Cited by
-
Translating quantitative theories of behavior into improved clinical treatments for problem behavior.Behav Processes. 2022 May;198:104639. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2022.104639. Epub 2022 Apr 9. Behav Processes. 2022. PMID: 35405305 Free PMC article.
-
Resurgence in humans: Reducing relapse by increasing generalization between treatment and testing.J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2019 Jul;45(3):338-349. doi: 10.1037/xan0000209. Epub 2019 Apr 29. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2019. PMID: 31033312 Free PMC article.
-
Relapse after incentivized choice treatment in humans: A laboratory model for studying behavior change.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2022 Apr;30(2):220-234. doi: 10.1037/pha0000443. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33507769 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral momentum theory fails to account for the effects of reinforcement rate on resurgence.J Exp Anal Behav. 2016 May;105(3):375-92. doi: 10.1002/jeab.207. J Exp Anal Behav. 2016. PMID: 27193242 Free PMC article.
-
Resurgence as Choice in Context: Treatment duration and on/off alternative reinforcement.J Exp Anal Behav. 2020 Jan;113(1):57-76. doi: 10.1002/jeab.563. Epub 2019 Nov 27. J Exp Anal Behav. 2020. PMID: 31777091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amsel A. Frustrative nonreward in partial reinforcement and discrimination learning: Some recent history and a theoretical extension. Psychological Review. 1962;69:306–328. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME. Context, ambiguity, and unlearning: Sources of relapse after behavioral extinction. Biological Psychiatry. 2002;52:976–986. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME. Context and behavioral processes in extinction. Learning and Memory. 2004;11:485–494. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME, Bolles RC. Contextual control of the extinction of conditioned fear. Learning and Motivation. 1979;10:445–466.
-
- Bouton ME, Rosengard C, Achenbach GG, Peck CA, Brooks DC. Effects of contextual conditioning and unconditional stimulus presentation on performance in appetitive conditioning. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology: Comparative and Physiological Psychology. 1993;46(B):63–95. - PubMed

