Allografts stimulate cross-reactive virus-specific memory CD8 T cells with private specificity
- PMID: 20659086
- PMCID: PMC2911646
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03161.x
Allografts stimulate cross-reactive virus-specific memory CD8 T cells with private specificity
Abstract
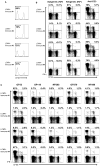
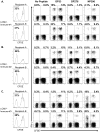
Viral infections have been associated with the rejection of transplanted allografts in humans and mice, and the induction of tolerance to allogeneic tissues in mice is abrogated by an ongoing viral infection and inhibited in virus-immune mice. One proposed mechanism for this 'heterologous immunity' is the induction of alloreactive T cell responses that cross-react with virus-derived antigens. These cross-reactive CD8 T cells are generated during acute viral infection and survive into memory, but their ability to partake in the immune response to allografts in vivo is not known. We show here that cross-reactive, virus-specific memory CD8 T cells from mice infected with LCMV proliferated in response to allografts. CD8 T cells specific to several LCMV epitopes proliferated in response to alloantigens, with the magnitude and hierarchy of epitope-specific responses varying with the private specificities of the host memory T cell repertoire, as shown by adoptive transfer studies. Last, we show that purified LCMV-specific CD8 T cells rejected skin allografts in SCID mice. These findings therefore implicate a potential role for heterologous immunity in virus-induced allograft rejection.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Direct visualization of cross-reactive effector and memory allo-specific CD8 T cells generated in response to viral infections.J Immunol. 2003 Apr 15;170(8):4077-86. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.8.4077. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12682237
-
Prior viral infection primes cross-reactive CD8+ T cells that respond to mouse heart allografts.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 8;14:1287546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1287546. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38143762 Free PMC article.
-
Private specificities of CD8 T cell responses control patterns of heterologous immunity.J Exp Med. 2005 Feb 21;201(4):523-33. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041337. Epub 2005 Feb 14. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 15710651 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of memory T cell proliferation under conditions of heterologous immunity and bystander stimulation.J Immunol. 2002 Jul 1;169(1):90-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.1.90. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12077233
-
Heterologous immunity between viruses.Immunol Rev. 2010 May;235(1):244-66. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00897.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20536568 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of renal allograft rejection reveals insights into intragraft TCR clonality.J Clin Invest. 2023 Jul 17;133(14):e170191. doi: 10.1172/JCI170191. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37227784 Free PMC article.
-
TCR cross-reactivity and allorecognition: new insights into the immunogenetics of allorecognition.Immunogenetics. 2012 Feb;64(2):77-85. doi: 10.1007/s00251-011-0590-0. Epub 2011 Dec 3. Immunogenetics. 2012. PMID: 22146829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer cells in lung transplantation.Thorax. 2019 Apr;74(4):397-404. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-212345. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Thorax. 2019. PMID: 30381399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of infection and tissue damage in solid-organ transplantation.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012 May 25;12(6):459-71. doi: 10.1038/nri3215. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22627862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ganciclovir transiently attenuates murine cytomegalovirus-associated renal allograft inflammation.Transplantation. 2011 Oct 15;92(7):759-66. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31822c6e89. Transplantation. 2011. PMID: 21878840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen JH, Mao YY, He Q, Wu JY, Lv R. The impact of pretransplant cytomegalovirus infection on acute renal allograft rejection. Transplant Proc. 2005;37(10):4203–4207. - PubMed
-
- Gaston JSH, Waer M. Virus-specific MHC-restricted T lymphocytes may initiate allograft rejection. Immunol Today. 1985;6(8):237–239. - PubMed
-
- Jakel KT, Loning T. Herpes virus infections, acute rejection, and transplant arteriosclerosis in human cardiac allografts. Transplant Proc. 1993;25(2):2029–2030. - PubMed
-
- Brehm MA, Daniels KA, Ortaldo JR, Welsh RM. Rapid conversion of effector mechanisms from NK to T cells during virus-induced lysis of allogeneic implants in vivo. J Immunol. 2005;174(11):6663–6671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

