Graft-versus-host disease: role of inflammation in the development of chromosomal abnormalities of keratinocytes
- PMID: 20659573
- PMCID: PMC3437935
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.07.014
Graft-versus-host disease: role of inflammation in the development of chromosomal abnormalities of keratinocytes
Abstract
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a major risk factor for secondary malignancy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the skin and mucous membranes are especially frequent in this setting where aneuploidy and tetraploidy are associated with aggressive disease. The current study is directed at the mechanism of neoplasia in this setting. Unmanipulated keratinocytes from areas of oral GVHD in 9 patients showed tetraploidy in 10% to 46% of cells when examined by florescein in situ hybridization (FISH). Keratinocytes isolated from biopsy sites of GVHD but not from normal tissue showed even greater numbers of tetraploid cells (mean = 78%, range: 15%-85%; N = 9) after culture. To mimic the inflammatory process in GVHD, allogeneic HLA-mismatched lymphocytes were mixed with normal keratinocytes. After 2 weeks, substantial numbers of aneuploid and tetraploid cells were evident in cultures with lymphocytes and with purified CD8 but not CD4 cells. Telomere length was substantially decreased in the lymphocyte-treated sample. No mutations were present in the p53 gene, although haploinsufficiency for p53 due to the loss of chromosome 17 was common in cells exposed to lymphocytes. These findings suggest that in GVHD, inflammation and repeated cell division correlate with the development of karyotypic abnormalities.
Copyright © 2010. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



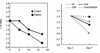
Left panel: Keratinocytes were cultured with PBLs as described in Methods and Materials and then passaged two times over the course of 17 days. Telomere length was then measured. PBLs caused a decrease in keratinocyte telomere, which was most prominent immediately following co-cultivation with lymphocytes.
Right panel: Keratinocytes were cultured with 30,000 purified CD4+, CD8+ and a mixture of similar numbers of CD4 and CD8 cells (i.e. 60,000 total lymphocytes), which were pre-incubated with cyclosporine. CD8+ cells showed the most dramatic change in telomere length.

References
-
- Bhatia S, Louie AD, Bhatia R, et al. Solid cancers after bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:464–471. - PubMed
-
- Ramsay HM, Reece SM, Fryer AA, Smith AG, Harden PN. Seven-Year Prospective Study of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer Incidence in U.K. Renal Transplant Recipients. Transplantation. 2007;84 - PubMed
-
- Socie G, Curtis RE, Deeg HJ, et al. New Malignant Diseases After Allogeneic Marrow Transplantation for Childhood Acute Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:348. - PubMed
-
- Ulrich C, Kanitakis J, Stockfleth E, Euvrard S. Skin cancer in organ transplant recipients- -where do we stand today? Am J Transplant. 2008;8:2192–2198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

