Inactivation of the orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell and tumor growth
- PMID: 20660371
- PMCID: PMC2988472
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1992
Inactivation of the orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell and tumor growth
Abstract
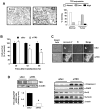
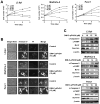
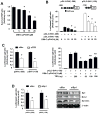
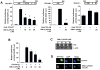
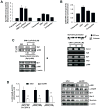
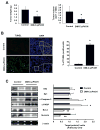
Activation of the orphan nuclear receptor TR3/Nur77 (NR4A1) promotes apoptosis and inhibits pancreatic tumor growth, but its endogenous function and the effects of its inactivation have yet to be determined. TR3 was overexpressed in human pancreatic tumors compared with nontumor tissue. Small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of TR3 or cell treatment with the TR3 antagonist 1,1-bis(3'-indolyl)-1-(p-hydroxyphenyl)methane (DIM-C-pPhOH) decreased proliferation, induced apoptosis, and decreased expression of antiapoptotic genes including Bcl-2 and survivin in pancreatic cancer cells. Survivin suppression was mediated by formation of a TR3-Sp1-p300 DNA binding complex on the proximal GC-rich region of the survivin promoter. When administered in vivo, DIM-C-pPhOH induced apoptosis and inhibited tumor growth in an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer, associated with inhibition of the same antiapoptotic markers observed in vitro. Our results offer preclinical validation of TR3 as a drug target for pancreatic cancer chemotherapy, based on the ability of TR3 inhibitors to block the growth of pancreatic tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Milbrandt J. Nerve growth factor induces a gene homologous to the glucocorticoid receptor gene. Neuron. 1988;1:183–8. - PubMed
-
- Giguere V. Orphan nuclear receptors: from gene to function. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:689–725. - PubMed
-
- McKenna NJ, O’Malley BW. Combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear receptors and coregulators. Cell. 2002;108:465–74. - PubMed
-
- Winoto A. Genes involved in T-cell receptor-mediated apoptosis of thymocytes and T-cell hybridomas. Semin Immunol. 1997;9:51–8. - PubMed
-
- Mullican SE, Zhang S, Konopleva M, et al. Abrogation of nuclear receptors Nr4a3 and Nr4a1 leads to development of acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med. 2007;13:730–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

