Chemoimmunotherapy with a modified hyper-CVAD and rituximab regimen improves outcome in de novo Philadelphia chromosome-negative precursor B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 20660823
- PMCID: PMC2940403
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.9456
Chemoimmunotherapy with a modified hyper-CVAD and rituximab regimen improves outcome in de novo Philadelphia chromosome-negative precursor B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
Purpose: The adverse prognosis of CD20 expression in adults with de novo precursor B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) prompted incorporation of monoclonal antibody therapy with rituximab into the intensive chemotherapy regimen hyper-CVAD (fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone). Other modifications (irrespective of CD20 expression) included early anthracycline intensification, alterations in number of risk-adapted intrathecal chemotherapy treatments for CNS prophylaxis, additional early and late intensifications, and extension of maintenance phase chemotherapy by 6 months.
Patients and methods: Two hundred eighty-two adolescents and adults with de novo Philadelphia chromosome (Ph)-negative precursor B-lineage ALL were treated with standard or modified hyper-CVAD regimens. The latter incorporated standard-dose rituximab if CD20 expression > or = 20%.
Results: The complete remission (CR) rate was 95% with 3-year rates of CR duration (CRD) and survival (OS) of 60% and 50%, respectively. In the younger (age < 60 years) CD20-positive subset, rates of CRD and OS were superior with the modified hyper-CVAD and rituximab regimens compared with standard hyper-CVAD (70% v 38%; P < .001% and 75% v 47%, P = .003). In contrast, rates of CRD and OS for CD20-negative counterparts treated with modified versus standard hyper-CVAD regimens were similar (72% v 68%, P = not significant [NS] and 64% v 65%, P = NS, respectively). Older patients with CD20-positive ALL did not benefit from rituximab-based chemoimmunotherapy (rates of CRD 45% v 50%, P = NS and OS 28% v 32%, P = NS, respectively), related in part to deaths in CR.
Conclusion: The incorporation of rituximab into the hyper-CVAD regimen appears to improve outcome for younger patients with CD20-positive Ph-negative precursor B-lineage ALL.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

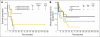
References
-
- Czuczman MS, Olejniczak S, Gowda A, et al. Acquirement of rituximab resistance in lymphoma cell lines is associated with both global CD20 gene and protein down-regulation regulated at the pretranscriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:1561–1570. - PubMed
-
- Jazirehi AR, Vega MI, Bonavida B. Development of rituximab-resistant lymphoma clones with altered cell signaling and cross-resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1270–1281. - PubMed
-
- Borowitz MJ, Shuster J, Carroll AJ, et al. Prognostic significance of fluorescence intensity of surface marker expression in childhood B- precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A Pediatric Oncology Group Study. Blood. 1997;89:3960–3966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

