p16INK4a expression in basal-like breast carcinoma
- PMID: 20661408
- PMCID: PMC2907122
p16INK4a expression in basal-like breast carcinoma
Abstract
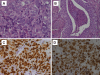
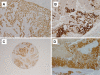
BLBC represents a distinctive group of invasive breast carcinomas with specific genotype and immunoprofile. BLBC is usually defined by gene expression profiling and is currently associated with poor outcome. BLBCs are estrogen receptor (ER) negative, progesterone receptor (PgR) negative, HER2 negative, and usually show a variable expression of basal cytokeratins (CKs), EGFR and CD117. p16(INK4a) is a tumor suppressor protein, encoded by the CDKN2A gene, which regulates cell cycle. The reported association of abnormalities in the p16/Rb pathway with increased risk of malignancy prompted us to determine the expression of p16(INK4a) in a group of BLBC; the results were compared with a group of high-grade invasive carcinoma (HG-IC) of breast. Tissue microarrays (TMA) were constructed in triplicate including 18 BLBC and 18 HG-IC. All BLBC cases were ER-/PgR-/HER2-. Seventeen (94%) BLBC were CK 5/6+/CK 14+; 14 (78%) BLCB showed EGFR expression and 13 (72%) were CD117 positive. BLBCs showed a strong positive reaction with p16(INK4a) antibody in 16 of 18 (89%) cases. Although the significance of p16(INK4a) expression in breast cancer is not fully understood, we have shown that p16(INK4a) is strongly expressed in breast cancers with basal-like phenotype. Since it is known that p16(INK4a) is associated with aggressive behavior in human carcinomas, these data suggest that p16(INK4a) play a role in the poor prognosis of BLBC.
Keywords: Breast cancer; HER2; basal cancer; estrogen receptor; immunohistochemistry; p16 INK4a; progesterone receptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
p16 promoter methylation, expression, and its association with estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 subtype of breast carcinoma.J Cancer Res Ther. 2019 Jul-Sep;15(5):1147-1154. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_472_18. J Cancer Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31603125
-
[Methylation and expression of gene p16INK4a and RB in breast carcinoma].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Jun;39(6):377-81. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21055153 Chinese.
-
Increased expression of senescence markers p14(ARF) and p16(INK4a) in breast cancer is associated with an increased risk of disease recurrence and poor survival outcome.Histopathology. 2016 Sep;69(3):479-91. doi: 10.1111/his.12948. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Histopathology. 2016. PMID: 26843058
-
Triple-negative breast cancer: disease entity or title of convenience?Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010 Dec;7(12):683-92. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.154. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20877296 Review.
-
Triple negative tumours: a critical review.Histopathology. 2008 Jan;52(1):108-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02889.x. Histopathology. 2008. PMID: 18171422 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive morphological study for basal-like breast carcinomas with comparison to nonbasal-like carcinomas.Diagn Pathol. 2012 Oct 20;7:145. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-145. Diagn Pathol. 2012. PMID: 23082819 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic Significance of P16 Immunohistochemical Expression Pattern in Women with Invasive Ductal Breast Carcinoma.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023 Apr;12(1):83-91. doi: 10.52547/rbmb.12.1.83. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37724141 Free PMC article.
-
Altered p16(INK4) and RB1 Expressions Are Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer.J Oncol. 2012;2012:957437. doi: 10.1155/2012/957437. Epub 2012 Apr 30. J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22619677 Free PMC article.
-
Senescent Stromal Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment: Victims or Accomplices?Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;15(7):1927. doi: 10.3390/cancers15071927. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential and correlated expressions of p16/p21/p27/p38 in mammary gland tumors of aged dogs.J Vet Sci. 2017 Dec 31;18(4):479-485. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.479. J Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 28927257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–752. - PubMed
-
- Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(8):1275–1281. - PubMed
-
- Reis-Filho JS, Tutt AN. Triple negative tumours: a critical review. Histopathology. 2008;52(1):108–118. - PubMed
-
- Bryan BB, Schnitt SJ, Collins LC. Ductal carcinoma in situ with basal-like phenotype: a possible precursor to invasive basal-like breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 2006;19(5):617–621. - PubMed
-
- Pintens S, Neven P, Drijkoningen M, Van Belle V, Moerman P, Christiaens MR, Smeets A, Wildiers H, Vanden Bempt I. Triple negative breast cancer: a study from the point of view of basal CK5/6 and HER-1. J Clin Pathol. 2009;62(7):624–628. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
