A comparative study of age-related hearing loss in wild type and insulin-like growth factor I deficient mice
- PMID: 20661454
- PMCID: PMC2907134
- DOI: 10.3389/fnana.2010.00027
A comparative study of age-related hearing loss in wild type and insulin-like growth factor I deficient mice
Abstract
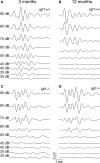
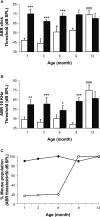
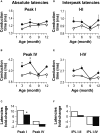
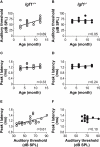
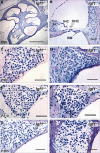
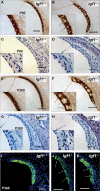
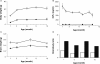
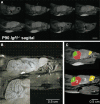
Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) belongs to the family of insulin-related peptides that fulfils a key role during the late development of the nervous system. Human IGF1 mutations cause profound deafness, poor growth and mental retardation. Accordingly, Igf1(-/-) null mice are dwarfs that have low survival rates, cochlear alterations and severe sensorineural deafness. Presbycusis (age-related hearing loss) is a common disorder associated with aging that causes social and cognitive problems. Aging is also associated with a decrease in circulating IGF-I levels and this reduction has been related to cognitive and brain alterations, although there is no information as yet regarding the relationship between presbycusis and IGF-I biodisponibility. Here we present a longitudinal study of wild type Igf1(+/+) and null Igf1(-/-) mice from 2 to 12 months of age comparing the temporal progression of several parameters: hearing, brain morphology, cochlear cytoarchitecture, insulin-related factors and IGF gene expression and IGF-I serum levels. Complementary invasive and non-invasive techniques were used, including auditory brainstem-evoked response (ABR) recordings and in vivo MRI brain imaging. Igf1(-/-) null mice presented profound deafness at all the ages studied, without any obvious worsening of hearing parameters with aging. Igf1(+/+) wild type mice suffered significant age-related hearing loss, their auditory thresholds and peak I latencies augmenting as they aged, in parallel with a decrease in the circulating levels of IGF-I. Accordingly, there was an age-related spiral ganglion degeneration in wild type mice that was not evident in the Igf1 null mice. However, the Igf1(-/-) null mice in turn developed a prematurely aged stria vascularis reminiscent of the diabetic strial phenotype. Our data indicate that IGF-I is required for the correct development and maintenance of hearing, supporting the idea that IGF-I-based therapies could contribute to prevent or ameliorate age-related hearing loss.
Keywords: Igf1−/− null mouse; aging; auditory brainstem responses; deafness; in vivo brain imaging; insulin-like factors; presbycusis; sensorineural deafness.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age-related functional and structural retinal modifications in the Igf1-/- null mouse.Neurobiol Dis. 2012 May;46(2):476-85. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.02.013. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Neurobiol Dis. 2012. PMID: 22402333
-
Insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2)-deficient mice show sensorineural hearing loss that is delayed by concomitant protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) loss of function.Mol Med. 2012 Mar 30;18(1):260-9. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00328. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22160220 Free PMC article.
-
The role of insulin-like growth factor-I in the physiopathology of hearing.Front Mol Neurosci. 2011 Jul 25;4:11. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00011. eCollection 2011. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21845174 Free PMC article.
-
Role of insulin-like growth factors in growth, development and feeding.World Rev Nutr Diet. 2013;106:60-5. doi: 10.1159/000342546. Epub 2013 Feb 11. World Rev Nutr Diet. 2013. PMID: 23428682 Review.
-
Neuroprotective role of insulin-like growth factor 1 in auditory and other nervous systems.Histol Histopathol. 2022 Jul;37(7):609-619. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-437. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Histol Histopathol. 2022. PMID: 35170014 Review.
Cited by
-
Translational implications of the interactions between hormones and age-related hearing loss.Hear Res. 2021 Mar 15;402:108093. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2020.108093. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Hear Res. 2021. PMID: 33097316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 modulates bioengineered tooth morphogenesis.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 23;9(1):368. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36863-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30675004 Free PMC article.
-
Altered resting-state functional connectivity of the anterior cingulate cortex in rats post noise exposure.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Oct;28(10):1547-1556. doi: 10.1111/cns.13896. Epub 2022 Jun 21. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35726754 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 on the Maintenance of Ribbon Synapses in Mouse Cochlear Explant Cultures.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Oct 8;14:571155. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.571155. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33132846 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroglial Involvement in Abnormal Glutamate Transport in the Cochlear Nuclei of the Igf1 -/- Mouse.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Mar 1;13:67. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00067. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30881288 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

