Quasispecies theory and the behavior of RNA viruses
- PMID: 20661479
- PMCID: PMC2908548
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001005
Quasispecies theory and the behavior of RNA viruses
Abstract
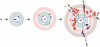
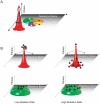
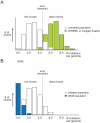
A large number of medically important viruses, including HIV, hepatitis C virus, and influenza, have RNA genomes. These viruses replicate with extremely high mutation rates and exhibit significant genetic diversity. This diversity allows a viral population to rapidly adapt to dynamic environments and evolve resistance to vaccines and antiviral drugs. For the last 30 years, quasispecies theory has provided a population-based framework for understanding RNA viral evolution. A quasispecies is a cloud of diverse variants that are genetically linked through mutation, interact cooperatively on a functional level, and collectively contribute to the characteristics of the population. Many predictions of quasispecies theory run counter to traditional views of microbial behavior and evolution and have profound implications for our understanding of viral disease. Here, we discuss basic principles of quasispecies theory and describe its relevance for our understanding of viral fitness, virulence, and antiviral therapeutic strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
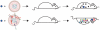
References
-
- Duffy S, Shackelton LA, Holmes EC. Rates of evolutionary change in viruses: patterns and determinants. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:267–276. - PubMed
-
- Beigel JH, Farrar J, Han AM, Hayden FG, Hyer R, et al. Avian influenza A (H5N1) infection in humans. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1374–1385. - PubMed
-
- Dawood FS, Jain S, Finelli L, Shaw MW, Lindstrom S, et al. Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:2605–2615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

