Real-time optical imaging using quantum dot and related nanocrystals
- PMID: 20662647
- PMCID: PMC3420008
- DOI: 10.2217/nnm.10.49
Real-time optical imaging using quantum dot and related nanocrystals
Abstract
Biomedical optical imaging is rapidly evolving because of its desirable features of rapid frame rates, high sensitivity, low cost, portability and lack of radiation. Quantum dots are attractive as imaging agents owing to their high brightness, and photo- and bio-stability. Here, the current status of in vitro and in vivo real-time optical imaging with quantum dots is reviewed. In addition, we consider related nanocrystals based on solid-state semiconductors, including upconverting nanoparticles and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer quantum dots. These particles can improve the signal-to-background ratio for real-time imaging largely by suppressing background signal. Although toxicity and biodistribution of quantum dots and their close relatives remain prime concerns for translation to human imaging, these agents have many desirable features that should be explored for medical purposes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
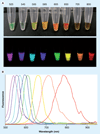




Similar articles
-
Quantum dots and multifunctional nanoparticles: new contrast agents for tumor imaging.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2006 Aug;1(2):209-17. doi: 10.2217/17435889.1.2.209. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2006. PMID: 17716110 Review.
-
Quantum dots in biomedical applications.Acta Biomater. 2019 Aug;94:44-63. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.022. Epub 2019 May 11. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31082570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Quantum dots and their applications in cancer research].Ai Zheng. 2006 May;25(5):651-6. Ai Zheng. 2006. PMID: 16687092 Review. Chinese.
-
[Application of functional quantum dots in cancer diagnosis and therapy: a review].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2013 Jan;29(1):10-20. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 23631114 Review. Chinese.
-
Semiconductor quantum dots for in vivo imaging.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2007 Aug;7(8):2567-81. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2007.628. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17685272 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the field of nanooncology.BMC Med. 2010 Dec 13;8:83. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-83. BMC Med. 2010. PMID: 21144040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-Wavelength Fluorescence Monitoring of Photodynamic Therapy: From Analytical Models to Clinical Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 19;13(22):5807. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225807. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830963 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo real-time lymphatic draining using quantum-dot optical imaging in mice.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2013 Jan-Feb;8(1):96-100. doi: 10.1002/cmmi.1487. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23109398 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical nature and structure of organic coating of quantum dots is crucial for their application in imaging diagnostics.Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:1719-32. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S17995. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011. PMID: 21980235 Free PMC article.
-
Current Status and Future Direction of Nanomedicine: Focus on Advanced Biological and Medical Applications.Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017 Jun;51(2):106-117. doi: 10.1007/s13139-016-0435-8. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28559935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoffman RM. The multiple uses of fluorescent proteins to visualize cancer in vivo. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2005;5(10):796–806. - PubMed
-
- Kitai T, Inomoto T, Miwa M, Shikayama T. Fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green for detecting sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2005;12(3):211–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
