Gene expression analysis after receptor tyrosine kinase activation reveals new potential melanoma proteins
- PMID: 20663135
- PMCID: PMC2912872
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-386
Gene expression analysis after receptor tyrosine kinase activation reveals new potential melanoma proteins
Abstract
Background: Melanoma is an aggressive tumor with increasing incidence. To develop accurate prognostic markers and targeted therapies, changes leading to malignant transformation of melanocytes need to be understood. In the Xiphophorus melanoma model system, a mutated version of the EGF receptor Xmrk (Xiphophorus melanoma receptor kinase) triggers melanomagenesis. Cellular events downstream of Xmrk, such as the activation of Akt, Ras, B-Raf or Stat5, were also shown to play a role in human melanomagenesis. This makes the elucidation of Xmrk downstream targets a useful method for identifying processes involved in melanoma formation.
Methods: Here, we analyzed Xmrk-induced gene expression using a microarray approach. Several highly expressed genes were confirmed by realtime PCR, and pathways responsible for their induction were revealed using small molecule inhibitors. The expression of these genes was also monitored in human melanoma cell lines, and the target gene FOSL1 was knocked down by siRNA. Proliferation and migration of siRNA-treated melanoma cell lines were then investigated.
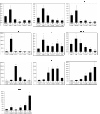
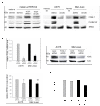
Results: Genes with the strongest upregulation after receptor activation were FOS-like antigen 1 (Fosl1), early growth response 1 (Egr1), osteopontin (Opn), insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (Igfbp3), dual-specificity phosphatase 4 (Dusp4), and tumor-associated antigen L6 (Taal6). Interestingly, most genes were blocked in presence of a SRC kinase inhibitor. Importantly, we found that FOSL1, OPN, IGFBP3, DUSP4, and TAAL6 also exhibited increased expression levels in human melanoma cell lines compared to human melanocytes. Knockdown of FOSL1 in human melanoma cell lines reduced their proliferation and migration.
Conclusion: Altogether, the data show that the receptor tyrosine kinase Xmrk is a useful tool in the identification of target genes that are commonly expressed in Xmrk-transgenic melanocytes and melanoma cell lines. The identified molecules constitute new possible molecular players in melanoma development. Specifically, a role of FOSL1 in melanomagenic processes is demonstrated. These data are the basis for future detailed analyses of the investigated target genes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The AP-1 transcription factor FOSL1 causes melanocyte reprogramming and transformation.Oncogene. 2017 Sep 7;36(36):5110-5121. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.135. Epub 2017 May 8. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28481878
-
Signalling by the oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinase Xmrk leads to activation of STAT5 in Xiphophorus melanoma.Oncogene. 1998 Jun 11;16(23):3047-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201844. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9662338
-
The oncogenic epidermal growth factor receptor variant Xiphophorus melanoma receptor kinase induces motility in melanocytes by modulation of focal adhesions.Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15;66(6):3145-52. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2667. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16540665
-
Signal transduction by the oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinase Xmrk in melanoma formation of Xiphophorus.Pigment Cell Res. 1997 Feb-Apr;10(1-2):34-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.1997.tb00463.x. Pigment Cell Res. 1997. PMID: 9170160 Review.
-
Genetic, biochemical and evolutionary facets of Xmrk-induced melanoma formation in the fish Xiphophorus.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2004 Jul;138(3):281-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2004.06.002. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15533786 Review.
Cited by
-
SuperDendrix algorithm integrates genetic dependencies and genomic alterations across pathways and cancer types.Cell Genom. 2022 Feb 9;2(2):100099. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2022.100099. Cell Genom. 2022. PMID: 35382456 Free PMC article.
-
NRF2 Enables EGFR Signaling in Melanoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 7;22(8):3803. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083803. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33916908 Free PMC article.
-
The MAPK pathway as an apoptosis enhancer in melanoma.Oncotarget. 2014 Jul 15;5(13):5040-53. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2079. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24970815 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-specificity protein phosphatase DUSP4 regulates response to MEK inhibition in BRAF wild-type melanoma.Br J Cancer. 2020 Feb;122(4):506-516. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0673-5. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Br J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31839677 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transmembrane 4 L Six Family Member 1 Suppresses Hormone Receptor--Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 27;13:770993. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.770993. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35153775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bittner M, Meltzer P, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Seftor E, Hendrix M, Radmacher M, Simon R, Yakhini Z, Ben-Dor A, Sampas N, Dougherty E, Wang E, Marincola F, Gooden C, Lueders J, Glatfelter A, Pollock P, Carpten J, Gillanders E, Leja D, Dietrich K, Beaudry C, Berens M, Alberts D, Sondak V. Molecular classification of cutaneous malignant melanoma by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;406(6795):536–540. doi: 10.1038/35020115. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hoek K, Rimm DL, Williams KR, Zhao H, Ariyan S, Lin A, Kluger HM, Berger AJ, Cheng E, Trombetta ES, Wu T, Niinobe M, Yoshikawa K, Hannigan GE, Halaban R. Expression profiling reveals novel pathways in the transformation of melanocytes to melanomas. Cancer Res. 2004;64(15):5270–5282. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0731. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

