Heterogeneity prevails: the state of clinical trial data management in Europe - results of a survey of ECRIN centres
- PMID: 20663165
- PMCID: PMC2918594
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-11-79
Heterogeneity prevails: the state of clinical trial data management in Europe - results of a survey of ECRIN centres
Abstract
Background: The use of Clinical Data Management Systems (CDMS) has become essential in clinical trials to handle the increasing amount of data that must be collected and analyzed. With a CDMS trial data are captured at investigator sites with "electronic Case Report Forms". Although more and more of these electronic data management systems are used in academic research centres an overview of CDMS products and of available data management and quality management resources for academic clinical trials in Europe is missing.
Methods: The ECRIN (European Clinical Research Infrastructure Network) data management working group conducted a two-part standardized survey on data management, software tools, and quality management for clinical trials. The questionnaires were answered by nearly 80 centres/units (with an overall response rate of 47% and 43%) from 12 European countries and EORTC.
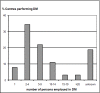
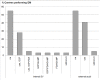
Results: Our survey shows that about 90% of centres have a CDMS in routine use. Of these CDMS nearly 50% are commercial systems; Open Source solutions don't play a major role. In general, solutions used for clinical data management are very heterogeneous: 20 different commercial CDMS products (7 Open Source solutions) in addition to 17/18 proprietary systems are in use. The most widely employed CDMS products are MACRO and Capture System, followed by solutions that are used in at least 3 centres: eResearch Network, CleanWeb, GCP Base and SAS. Although quality management systems for data management are in place in most centres/units, there exist some deficits in the area of system validation.
Conclusions: Because the considerable heterogeneity of data management software solutions may be a hindrance to cooperation based on trial data exchange, standards like CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standard Consortium) should be implemented more widely. In a heterogeneous environment the use of data standards can simplify data exchange, increase the quality of data and prepare centres for new developments (e.g. the use of EHR for clinical research). Because data management and the use of electronic data capture systems in clinical trials are characterized by the impact of regulations and guidelines, ethical concerns are discussed. In this context quality management becomes an important part of compliant data management. To address these issues ECRIN will establish certified data centres to support electronic data management and associated compliance needs of clinical trial centres in Europe.
Figures

References
-
- Hyde A. The changing face of electronic data capture: from remote data entry to direct data capture. Drug Inf J. 1998;32(4):1089–1092.
-
- Kubick WR. The elegant machine: applying technology to optimize clinical trials. Drug Inf J. 1998;32(4):861–869.
-
- Keim E, Sippel H, Eich HP, Ohmann C. Collection of data in clinical studies via internet. Stud Health Tech Information. 1997;43:57–60. - PubMed
-
- CenterWatch. EDC adoption in clinical trials: a 2008 analysis. Bio-ITworld. 2008. http://www.bio-itworld.com/EDC-Adoption.aspx?terms=health accessed 05.05.10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

