Characterization of proteinases from the midgut of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus involved in the generation of antimicrobial peptides
- PMID: 20663211
- PMCID: PMC2921360
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-3-63
Characterization of proteinases from the midgut of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus involved in the generation of antimicrobial peptides
Abstract
Background: Hemoglobin is a rich source of biologically active peptides, some of which are potent antimicrobials (hemocidins). A few hemocidins have been purified from the midgut contents of ticks. Nonetheless, how antimicrobials are generated in the tick midgut and their role in immunity is still poorly understood. Here we report, for the first time, the contribution of two midgut proteinases to the generation of hemocidins.
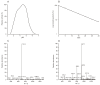
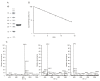
Results: An aspartic proteinase, designated BmAP, was isolated from the midgut of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus using three chromatographic steps. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction revealed that BmAP is restricted to the midgut. The other enzyme is a previously characterized midgut cathepsin L-like cysteine proteinase designated BmCL1. Substrate specificities of native BmAP and recombinant BmCL1 were mapped using a synthetic combinatorial peptide library and bovine hemoglobin. BmCL1 preferred substrates containing non-polar residues at P2 subsite and polar residues at P1, whereas BmAP hydrolysed substrates containing non-polar amino acids at P1 and P1'.
Conclusions: BmAP and BmCL1 generate hemocidins from hemoglobin alpha and beta chains in vitro. We postulate that hemocidins may be important for the control of tick pathogens and midgut flora.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Blood anticlotting activity of a Rhipicephalus microplus cathepsin L-like enzyme.Biochimie. 2019 Aug;163:12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2019.04.025. Epub 2019 May 3. Biochimie. 2019. PMID: 31059753
-
Boophilus microplus cathepsin L-like (BmCL1) cysteine protease: specificity study using a peptide phage display library.Vet Parasitol. 2011 Sep 27;181(2-4):291-300. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.04.003. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Vet Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21536386
-
Purification and characterization of Hb 98-114: a novel hemoglobin-derived antimicrobial peptide from the midgut of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus.Peptides. 2012 Sep;37(1):120-7. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2012.05.017. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Peptides. 2012. PMID: 22749988
-
Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus embryo proteins as target for tick vaccine.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012 Jul 15;148(1-2):149-56. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 May 7. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 21620488 Review.
-
Review of cattle ticks (Acari, Ixodida) in Ivory Coast and geographic distribution of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, an emerging tick in West Africa.Exp Appl Acarol. 2017 Apr;71(4):355-369. doi: 10.1007/s10493-017-0129-7. Epub 2017 May 11. Exp Appl Acarol. 2017. PMID: 28497303 Review.
Cited by
-
Culex quinquefasciatus storage proteins.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 29;8(10):e77664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077664. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24204911 Free PMC article.
-
A snapshot of the Ixodes scapularis degradome.Gene. 2011 Aug 15;482(1-2):78-93. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.04.008. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Gene. 2011. PMID: 21596113 Free PMC article.
-
Novel pseudo-aspartic peptidase from the midgut of the tick Rhipicephalus microplus.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 24;9(1):435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36849-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30679545 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating In Vitro and In Silico Approaches to Assess Monotheca buxifolia Plant Extract against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Sarcoptes scabiei.Molecules. 2023 Oct 4;28(19):6930. doi: 10.3390/molecules28196930. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37836773 Free PMC article.
-
Mialostatin, a Novel Midgut Cystatin from Ixodes ricinus Ticks: Crystal Structure and Regulation of Host Blood Digestion.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 20;22(10):5371. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105371. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34065290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lara FA, Lins U, Paiva-Silva G, Almeida IC, Braga CM, Miguens FC, Oliveira PL, Dansa-Petretski M. A new intracellular pathway of haem detoxification in the midgut of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus: aggregation inside a specialized organelle, the hemosome. J Exp Biol. 2003;206:1707–15. doi: 10.1242/jeb.00334. - DOI - PubMed

