Pre-operative inspiratory muscle training preserves postoperative inspiratory muscle strength following major abdominal surgery - a randomised pilot study
- PMID: 20663275
- PMCID: PMC3229384
- DOI: 10.1308/003588410X12771863936648
Pre-operative inspiratory muscle training preserves postoperative inspiratory muscle strength following major abdominal surgery - a randomised pilot study
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this pilot study was to assess the effect of pre-operative inspiratory muscle training (IMT) on respiratory variables in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery.
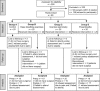
Patients and methods: Respiratory muscle strength (maximum inspiratory [MIP] and expiratory [MEP] mouth pressure) and pulmonary functions were measured at least 2 weeks before surgery in 80 patients awaiting major abdominal surgery. Patients were then allocated randomly to one of four groups (Group A, control; Group B, deep breathing exercises; Group C, incentive spirometry; Group D, specific IMT). Patients in groups B, C and D were asked to train twice daily, each session lasting 15 min, for at least 2 weeks up to the day before surgery. Outcome measurements were made immediately pre-operatively and postoperatively.
Results: In groups A, B and C, MIP did not increase from baseline to pre-operative assessments. In group D, MIP increased from 51.5 cmH(2)O (median) pre-training to 68.5 cmH(2)O (median) post-training pre-operatively (P < 0.01). Postoperatively, groups A, B and C showed a fall in MIP from baseline (P < 0.01, P < 0.01) and P = 0.06, respectively). No such significant reduction in postoperative MIP was seen in group D (P = 0.36).
Conclusions: Pre-operative specific IMT improves MIP pre-operatively and preserves it postoperatively. Further studies are required to establish if this is associated with reduced pulmonary complications.
References
-
- Teba L, Omert LA. Postoperative respiratory insufficiency. Am Fam Phys. 1995;51:1473–80. - PubMed
-
- Roukema JA, Carol EJ, Prins JG. The prevention of pulmonary complications after upper abdominal surgery in patients with noncompromised pulmonary status. Arch Surg. 1988;123:30–4. - PubMed
-
- Brooks-Brunn JA. Postoperative atelectasis and pneumonia. Heart Lung. 1995;24:94–115. - PubMed
-
- Weiner P, Zeidan F, Zamir D, Pelled B, Waizman J, et al. Prophylactic inspiratory muscle training in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft. World J Surg. 1998;22:427–31. - PubMed
-
- Nomori H, Kobayashi R, Fuyuno G, Morinaga S, Yashima H. Preoperative respiratory muscle training. Assessment in thoracic surgery patients with special reference to postoperative pulmonary complications. Chest. 1994;105:1782–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical