A case of multiple intracranial aneurysms with unruptured associated aneurysms and newly developed ruptured aneurysm
- PMID: 20663357
- PMCID: PMC3621065
- DOI: 10.1177/159101990100700313
A case of multiple intracranial aneurysms with unruptured associated aneurysms and newly developed ruptured aneurysm
Abstract
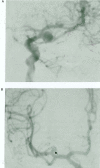
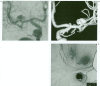
We report a case of mirror aneurysms at the middle cerebral artery bifurcation with rupture on the left side. After six years, the patient had subarachnoid haemorrhage from a de novo aneurysm which developed separate from but adjacent to the already present aneurysm on the right side. The mechanism of development of multiple aneurysms, especially of the mirror-image type cannot be explained based only on haemodynamic factors and congenital segmental arterial vulnerability which is generalised than focal is highly likely. The sequence of development of aneurysms in this patient along with existing knowledge regarding rupture of aneurysms in conditions like polycystic kidney disease raise questions about the current trend of treating all patients with coincidental, unruptured aneurysms as they may never bleed from such aneurysms but could still be at risk of SAH from newly developing aneurysms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive anatomical factors for rupture in middle cerebral artery mirror bifurcation aneurysms.J Neurosurg. 2018 Jun;128(6):1799-1807. doi: 10.3171/2017.2.JNS162705. Epub 2017 Aug 25. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28841119
-
Risk of hemorrhage from de novo cerebral aneurysms.J Neurosurg. 2013 Jan;118(1):58-62. doi: 10.3171/2012.9.JNS111512. Epub 2012 Oct 12. J Neurosurg. 2013. PMID: 23061385
-
The safety of vasopressor-induced hypertension in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients with coexisting unruptured, unprotected intracranial aneurysms.J Neurosurg. 2015 Oct;123(4):862-71. doi: 10.3171/2014.12.JNS141201. Epub 2015 Jul 24. J Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 26207606
-
Current Management of Mirror Distal Anterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms in Association with Multiple Aneurysms: Case Report with Literature Review.World Neurosurg. 2019 Oct;130:324-334. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.07.084. Epub 2019 Jul 16. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31323413 Review.
-
Unruptured intracranial aneurysms.J Neuroradiol. 2003 Dec;30(5):336-50. J Neuroradiol. 2003. PMID: 14752379 Review.
Cited by
-
A Rare Case Report of Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms with Factor VII Deficiency.Asian J Neurosurg. 2018 Jul-Sep;13(3):814-816. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_252_16. Asian J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30283554 Free PMC article.
-
Suggested connections between risk factors of intracranial aneurysms: a review.Ann Biomed Eng. 2013 Jul;41(7):1366-83. doi: 10.1007/s10439-012-0723-0. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013. PMID: 23242844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schievink WI. Intracranial aneurysms. New England J of Med. 1997;336(1):28–40. - PubMed
-
- Yong-Zhong G, van Alphen HA. Pathogenesis and histopathology of saccular aneurysms: review of the literature. Neurol Res. 1990;12(4):249–255. - PubMed
-
- Sekhar LN, Heros RC. Origin, growth and rupture of saccular aneurysms: a review. Neurosurgery. 1981;8(2):248–260. - PubMed
-
- Stebhens WE. Etiology of intracranial berry aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1989;70(6):823–831. - PubMed
-
- Pia HW, Langmaid C, Zierski J. Cerebral aneurysms. Advances in diagnosis and therapy. Springer Verlag; 1979.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

