Association between foot temperature and sudomotor dysfunction in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 20663441
- PMCID: PMC2909509
- DOI: 10.1177/193229681000400406
Association between foot temperature and sudomotor dysfunction in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background and aims: Increased foot skin temperature has been described as a feature of diabetic neuropathy. The aim of this present study was to investigate the association between foot temperature and sudomotor dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
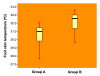
Patients and methods: This study included 51 patients (group A: 25 men, mean age 61.14 +/- 6.11 years) without sudomotor dysfunction and 52 patients (group B: 25 men, mean age 59.54 +/- 6.18 years) with sudomotor dysfunction. Sudomotor dysfunction was defined as time until complete Neuropad color change from blue to pink exceeding 600 s in at least one foot. Time until complete color change of the test was also recorded. Foot skin temperature was measured with a handheld infrared thermometer on the plantar aspect of the foot at the level of the first metatarsal head.
Results: On both feet, temperature was significantly higher in group B than in group A (right foot, group A versus group B, 30.62 +/- 1.13 degrees C versus 32.12 +/- 1.06 degrees C, p < .001; left foot, group A versus group B, 30.65 +/- 1.06 degrees C versus 32.19 +/- 1.10 degrees C, p < .001). There was a significant positive correlation between time to complete Neuropad color change and foot skin temperature (right foot, r = 0.742, p < .001; left foot, r = 0.758, p < .001), which was confirmed in both groups.
Conclusions: Patients with sudomotor dysfunction have significantly higher foot temperature than those without sudomotor dysfunction. Foot temperature is positively correlated with severity of sudomotor dysfunction, as evaluated by the time to complete Neuropad color change.
2010 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reproducibility of the new indicator test for sudomotor function (Neuropad) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: short communication.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2005 Dec;113(10):577-81. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-872912. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2005. PMID: 16320155 Clinical Trial.
-
Thermoregulatory sudomotor dysfunction and diabetic neuropathy develop in parallel in at-risk feet.Diabet Med. 2008 Apr;25(4):413-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02395.x. Epub 2008 Mar 13. Diabet Med. 2008. PMID: 18341593
-
Evaluation of a new indicator test for sudomotor function (Neuropad) in the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetic patients.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2005 Apr;113(4):195-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-837735. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2005. PMID: 15891953
-
Increased serum levels of uric acid are associated with sudomotor dysfunction in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Exp Diabetes Res. 2011;2011:346051. doi: 10.1155/2011/346051. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Exp Diabetes Res. 2011. PMID: 21941527 Free PMC article.
-
Foot temperature in type 2 diabetic patients with or without peripheral neuropathy.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2009 Jan;117(1):44-7. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1081498. Epub 2008 Aug 25. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 18726865
Cited by
-
Management of diabetic foot ulcers.Diabetes Ther. 2012 Nov;3(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s13300-012-0004-9. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Diabetes Ther. 2012. PMID: 22529027 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of AI-Powered Thermography to Detect Early Plantar Thermal Abnormalities in Patients With Diabetes: Cross-Sectional Observational Study.JMIR Diabetes. 2025 Jun 13;10:e65209. doi: 10.2196/65209. JMIR Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40512999 Free PMC article.
-
Preventative Sensor-Based Remote Monitoring of the Diabetic Foot in Clinical Practice.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 27;23(15):6712. doi: 10.3390/s23156712. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571496 Free PMC article.
-
Repeatability of infrared plantar thermography in diabetes patients: a pilot study.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013 Sep 1;7(5):1130-7. doi: 10.1177/193229681300700505. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 24124938 Free PMC article.
-
Plantar thermography is useful in the early diagnosis of diabetic neuropathy.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012 Dec;67(12):1419-25. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2012(12)12. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012. PMID: 23295596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bharara M, Cobb JE, Claremont DJ. Thermography and thermometry in the assessment of diabetic neuropathic foot: a case for furthering the role of thermal techniques. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2006;5(4):250–260. - PubMed
-
- Naicker AS, Roohi SA, Lee CS, Chan WH, Tay LS, Din XJ, Eow LH. Alteration of foot temperature in diabetic neuropathy: is it another piece of puzzle? Med J Malaysia. 2006;61(Suppl A):10–13. - PubMed
-
- Boyko EJ, Ahroni JH, Stensel VL. Skin temperature in the neuropathic diabetic foot. J Diabetes Complications. 2001;15(5):260–264. - PubMed
-
- Boulton AJ. The diabetic foot: from art to science. The 18th Camillo Golgi lecture. Diabetologia. 2004;47(8):1343–1353. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical