Thermal imaging today and its relevance to diabetes
- PMID: 20663449
- PMCID: PMC2909517
- DOI: 10.1177/193229681000400414
Thermal imaging today and its relevance to diabetes
Abstract
From the historic and simple assessment of temperature by the clinical thermometer, modern infrared technology has opened up new perspectives, especially in the use of thermal imaging to map body surface temperature with a remote sensing camera. Since the 1960s, there is now a greater understanding of thermal physiology and the relationship between skin temperature and blood perfusion. Furthermore, the examination technique, and the advantages of computer-aided digital imaging has greatly improved the reliability of this technology in medicine. Studies in diabetology have shown the value of this new facility and its relevance to clinical assessment of peripheral perfusion and tissue viability.
2010 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures

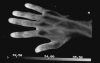
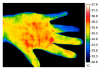
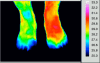
Similar articles
-
Infrared thermal imaging in medicine.Physiol Meas. 2012 Mar;33(3):R33-46. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/33/3/R33. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Physiol Meas. 2012. PMID: 22370242 Review.
-
Pathophysiological expression and analysis of far infrared thermal images.IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 1998 Jul-Aug;17(4):34-42. doi: 10.1109/51.687961. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 1998. PMID: 9672808 No abstract available.
-
Thermography-based blood flow imaging in human skin of the hands and feet: a spectral filtering approach.Physiol Meas. 2017 Feb;38(2):272-288. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/aa4eaf. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Physiol Meas. 2017. PMID: 28099162
-
Dynamic thermographic imaging method for quantifying dermal perfusion: potential and limitations.Med Biol Eng Comput. 1989 Sep;27(5):496-501. doi: 10.1007/BF02441468. Med Biol Eng Comput. 1989. PMID: 2622230
-
Functional infrared imaging in medicine: a quantitative diagnostic approach.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006;2006:224-7. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2006.260267. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006. PMID: 17946387 Review.
Cited by
-
Plantar thermography is useful in the early diagnosis of diabetic neuropathy.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012 Dec;67(12):1419-25. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2012(12)12. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012. PMID: 23295596 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of low-level laser therapy on blood flow and oxygen- hemoglobin saturation of the foot skin in healthy subjects: a pilot study.Laser Ther. 2013;22(1):21-30. doi: 10.5978/islsm.13-or-03. Laser Ther. 2013. PMID: 24155546 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal Imaging of the Tongue Surface as a Predictive Method in the Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 11;24(8):2447. doi: 10.3390/s24082447. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38676064 Free PMC article.
-
Infrared Thermal Imaging of Patients With Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infection: Mixed Methods Analysis.Interact J Med Res. 2021 Aug 19;10(3):e22524. doi: 10.2196/22524. Interact J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34420912 Free PMC article.
-
Best practices for standardized performance testing of infrared thermographs intended for fever screening.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 19;13(9):e0203302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203302. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30231046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wunderlich CA. In: On the temperature in diseases, a manual of medical thermometry. Woodman WB, translator. London: The New Sydenham Society; 1871.
-
- Wolfe WL. Infrared imaging devices in infrared medical radiography. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1964;121:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Houdas Y, Ring EF. Human body temperature, its measurement and regulation. New York: Plenum Press; 1982.
-
- Ring EF, Ammer K. The technique of infrared imaging in medicine. Thermol Int. 2000;10(1):7–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

