Proposed clinical application for tuning fuzzy logic controller of artificial pancreas utilizing a personalization factor
- PMID: 20663457
- PMCID: PMC2909525
- DOI: 10.1177/193229681000400422
Proposed clinical application for tuning fuzzy logic controller of artificial pancreas utilizing a personalization factor
Abstract
Background: Physicians tailor insulin dosing based on blood glucose goals, response to insulin, compliance, lifestyle, eating habits, daily schedule, and fear of and ability to detect hypoglycemia.
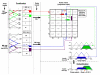
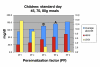
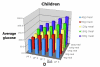
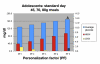
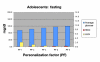
Method: We introduce a method that allows a physician to tune a fuzzy logic controller (FLC) artificial pancreas (AP) for a particular patient. It utilizes the physician's judgment and weighing of various factors. The personalization factor (PF) is a scaling of the dose produced by the FLC and is used to customize the dosing. The PF has discrete values of 1 through 5. The proposed method was developed using a database of results from 30 University of Virginia/Padova Metabolic Simulator in silico subjects (10 adults, 10 adolescents, and 10 children). Various meal sizes and timing were used to provide the physician information on which to base an initial dosing regimen and PF. Future decisions on dosing aggressiveness using the PF would be based on the patient's data at follow-up.
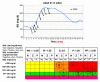
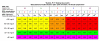
Results: Three examples of a wide variation in diabetes situations are given to illustrate the physician's thought process when initially configuring the AP system for a specific patient.
Conclusions: Fuzzy logic controllers are developed by encoding human expertise into the design of the controller. The FLC methodology allows for the real-time scaling of doses without compromising the integrity of the dosing rules matrix. The use of the PF to individualize the AP system is enabled by the fuzzy logic development methodology.
2010 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures
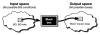









References
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. New Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):977–86. - PubMed
-
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Artificial Pancreas Project http://www.jdrf.org/index.cfm?page_id=104576. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zadeh LA. Fuzzy sets. Inform Control. 1965;8:338–353.
-
- The MathWorks Fuzzy inference systems. http://www.mathworks.com/access/helpdesk/help/toolbox/fuzzy/fp351dup8.html.
-
- Mamdani EH. Application of fuzzy algorithms for control of simple dynamic plant. Proc IEE. 1974;121(12):1585–1588.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

