Separate roles of structured and unstructured regions of Y-family DNA polymerases
- PMID: 20663485
- PMCID: PMC3103052
- DOI: 10.1016/S1876-1623(08)78004-0
Separate roles of structured and unstructured regions of Y-family DNA polymerases
Abstract
All organisms have multiple DNA polymerases specialized for translesion DNA synthesis (TLS) on damaged DNA templates. Mammalian TLS DNA polymerases include Pol eta, Pol iota, Pol kappa, and Rev1 (all classified as "Y-family" members) and Pol zeta (a "B-family" member). Y-family DNA polymerases have highly structured catalytic domains; however, some of these proteins adopt different structures when bound to DNA (such as archaeal Dpo4 and human Pol kappa), while others maintain similar structures independently of DNA binding (such as archaeal Dbh and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pol eta). DNA binding-induced structural conversions of TLS polymerases depend on flexible regions present within the catalytic domains. In contrast, noncatalytic regions of Y-family proteins, which contain multiple domains and motifs for interactions with other proteins, are predicted to be mostly unstructured, except for short regions corresponding to ubiquitin-binding domains. In this review we discuss how the organization of structured and unstructured regions in TLS polymerases is relevant to their regulation and function during lesion bypass.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




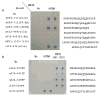


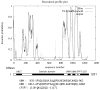
Similar articles
-
Mouse Rev1 protein interacts with multiple DNA polymerases involved in translesion DNA synthesis.EMBO J. 2003 Dec 15;22(24):6621-30. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg626. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 14657033 Free PMC article.
-
Translesion Synthesis of the N(2)-2'-Deoxyguanosine Adduct of the Dietary Mutagen IQ in Human Cells: Error-Free Replication by DNA Polymerase κ and Mutagenic Bypass by DNA Polymerases η, ζ, and Rev1.Chem Res Toxicol. 2016 Sep 19;29(9):1549-59. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00221. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27490094 Free PMC article.
-
Translesion synthesis across abasic lesions by human B-family and Y-family DNA polymerases α, δ, η, ι, κ, and REV1.J Mol Biol. 2010 Nov 19;404(1):34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.09.015. Epub 2010 Oct 1. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20888339 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic translesion synthesis DNA polymerases: specificity of structure and function.Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:317-53. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133250. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15952890 Review.
-
Filling gaps in translesion DNA synthesis in human cells.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2018 Dec;836(Pt B):127-142. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2018.02.004. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2018. PMID: 30442338 Review.
Cited by
-
Both high-fidelity replicative and low-fidelity Y-family polymerases are involved in DNA rereplication.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Feb;35(4):699-715. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01153-14. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25487575 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing the Catalytic Activities and Interactions of Eukaryotic Translesion Synthesis Polymerases.Methods Enzymol. 2017;592:329-356. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 May 8. Methods Enzymol. 2017. PMID: 28668126 Free PMC article.
-
Different types of interaction between PCNA and PIP boxes contribute to distinct cellular functions of Y-family DNA polymerases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 18;43(16):7898-910. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv712. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26170230 Free PMC article.
-
Translesion Synthesis: Insights into the Selection and Switching of DNA Polymerases.Genes (Basel). 2017 Jan 10;8(1):24. doi: 10.3390/genes8010024. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28075396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporally distinct post-replicative repair mechanisms fill PRIMPOL-dependent ssDNA gaps in human cells.Mol Cell. 2021 Oct 7;81(19):4026-4040.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.09.013. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34624216 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

