Occludin is required for cytokine-induced regulation of tight junction barriers
- PMID: 20663912
- PMCID: PMC2915885
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.065581
Occludin is required for cytokine-induced regulation of tight junction barriers
Abstract
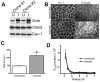
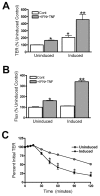
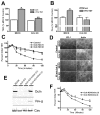
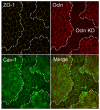
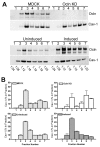
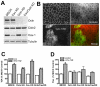
The function of occludin remains elusive. Proposed roles include maintenance of tight junction barriers, signaling and junction remodeling. To investigate a potential role in mediating cytokine-induced changes in barrier properties, we measured barrier responses to interferon-gamma plus TNFalpha in control, occludin-overexpressing and occludin knockdown MDCK II monolayers. MDCK cells show a complex response to cytokines characterized by a simultaneous increase in the transepithelial electrical resistance and a decrease in the barrier for large solutes. We observed that overexpression of occludin increased and occludin knockdown decreased sensitivity to cytokines as assessed by both these parameters. It is known that caveolin-1 interacts with occludin and is implicated in several models of cytokine-dependent barrier disruption; we found that occludin knockdown altered the subcellular distribution of caveolin-1 and that partitioning of caveolin into detergent-insoluble lipid rafts was influenced by changing occludin levels. Knockdown of caveolin decreased the cytokine-induced flux increase, whereas the increase in the electrical barrier was unaltered; the effect of double knockdown of occludin and caveolin was similar to that of occludin single knockdown, consistent with the possibility that they function in the same pathway. These results demonstrate that occludin is required for cells to transduce cytokine-mediated signals that either increase the electrical barrier or decrease the large solute barrier, possibly by coordinating the functions of caveolin-1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Occludin is a functional component of the tight junction.J Cell Sci. 1996 Sep;109 ( Pt 9):2287-98. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.9.2287. J Cell Sci. 1996. PMID: 8886979
-
Caveolin-1-dependent occludin endocytosis is required for TNF-induced tight junction regulation in vivo.J Cell Biol. 2010 Apr 5;189(1):111-26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200902153. Epub 2010 Mar 29. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20351069 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin binds independently to claudin-2 and occludin.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Jun;1257:103-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06535.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22671595
-
Occludin and the functions of tight junctions.Int Rev Cytol. 1999;186:117-46. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61052-9. Int Rev Cytol. 1999. PMID: 9770298 Review.
-
Molecular analyses of tight junction physiology: insights and paradoxes.J Membr Biol. 1998 Jun 1;163(3):159-67. doi: 10.1007/s002329900380. J Membr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9625773 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Claudins: Gatekeepers of lung epithelial function.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Jun;42:47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.04.009. Epub 2015 May 4. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25951797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of paracellular permeability: factors and mechanisms.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Nov;40(11):6123-42. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2724-y. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24062072 Review.
-
Autophagy Reduces the Degradation and Promotes Membrane Localization of Occludin to Enhance the Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier against Paracellular Macromolecule Flux.J Crohns Colitis. 2023 Apr 3;17(3):433-449. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac148. J Crohns Colitis. 2023. PMID: 36219473 Free PMC article.
-
The psychoactive drug of abuse mephedrone differentially disrupts blood-brain barrier properties.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Mar 1;18(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02116-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 33648543 Free PMC article.
-
The serine protease-mediated increase in intestinal epithelial barrier function is dependent on occludin and requires an intact tight junction.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;311(3):G466-79. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00441.2015. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27492333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balda M. S., Whitney J. A., Flores C., Gonzalez S., Cereijido M., Matter K. (1996). Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J. Cell Biol. 134, 1031-1049 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balda M. S., Flores-Maldonado C., Cereijido M., Matter K. (2000). Multiple domains of occludin are involved in the regulation of paracellular permeability. J. Cell Biochem. 78, 85-96 - PubMed
-
- Clayburgh D. R., Barrett T. A., Tang Y., Meddings J. B., Van Eldik L. J., Watterson D. M., Clarke L. L., Mrsny R. J., Turner J. R. (2005). Epithelial myosin light chain kinase-dependent barrier dysfunction mediates T cell activation-induced diarrhea in vivo. J. Clin. Invest 115, 2702-2715 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

