Busulfan 12 mg/kg plus melphalan 140 mg/m2 versus melphalan 200 mg/m2 as conditioning regimens for autologous transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients included in the PETHEMA/GEM2000 study
- PMID: 20663944
- PMCID: PMC2966914
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2010.028027
Busulfan 12 mg/kg plus melphalan 140 mg/m2 versus melphalan 200 mg/m2 as conditioning regimens for autologous transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients included in the PETHEMA/GEM2000 study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare the long-term safety and efficacy of oral busulfan 12 mg/kg plus melphalan 140 mg/m(2) and melphalan 200 mg/m(2) as conditioning regimens for autologous stem cell transplantation in newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma in the GEM2000 study.
Design and methods: The first 225 patients received oral busulfan 12 mg/kg plus melphalan 140 mg/m(2); because of a high frequency of veno-occlusive disease, the protocol was amended and a further 542 patients received melphalan 200 mg/m(2).
Results: Engraftment and hospitalization times were similar in both groups. Oral busulfan 12 mg/kg plus melphalan 140 mg/m(2) resulted in higher transplant-related mortality (8.4% versus 3.5%; P=0.002) due to the increased frequency of veno-occlusive disease in this group. Response rates were similar in both arms. With respective median follow-ups of 72 and 47 months, the median progression-free survival was significantly longer with busulfan plus melphalan (41 versus 31 months; P=0.009), although survival was similar to that in the melphalan 200 mg/m(2) group. However, access to novel agents as salvage therapy after relapse/progression was significantly lower for patients receiving busulfan plus melphalan (43%) than for those receiving melphalan 200 mg/m(2) (58%; P=0.01).
Conclusions: Conditioning with oral busulfan 12 mg/kg plus melphalan 140 mg/m(2) was associated with longer progression-free survival but equivalent survival to that achieved with melphalan 200 mg/m(2) but this should be counterbalanced against the higher frequency of veno-occlusive disease-related deaths. This latter fact together with the limited access to novel salvage therapies in patients conditioned with oral busulfan 12 mg/kg plus melphalan 140 mg/m(2) may explain the absence of a survival difference. Oral busulfan was used in the present study; use of the intravenous formulation may reduce toxicity and result in greater efficacy, and warrants further investigation in myeloma patients. (Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT00560053).
Figures

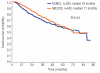
References
-
- Attal M, Harousseau JL, Stoppa AM, Sotto JJ, Fuzibet JG, Rossi JF, et al. A prospective, randomized trial of autologous bone marrow transplantation and chemotherapy in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 1996;335(2):91–7. - PubMed
-
- Child JA, Morgan GJ, Davies FE, Owen RG, Bell SE, Hawkins K, et al. High-dose chemotherapy with hematopoietic stem-cell rescue for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(19):1875–83. - PubMed
-
- McElwain TJ, Powles RL. High-dose intravenous melphalan for plasma-cell leukaemia and myeloma. Lancet. 1983;2(8354):822–4. - PubMed
-
- Selby PJ, McElwain TJ, Nandi AC, Perren TJ, Powles RL, Tillyer CR, et al. Multiple myeloma treated with high dose intravenous melphalan. Br J Haematol. 1987;66(1):55–62. - PubMed

