Direct transcriptional control of the Arabidopsis immune receptor FLS2 by the ethylene-dependent transcription factors EIN3 and EIL1
- PMID: 20663954
- PMCID: PMC2922558
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1003347107
Direct transcriptional control of the Arabidopsis immune receptor FLS2 by the ethylene-dependent transcription factors EIN3 and EIL1
Abstract
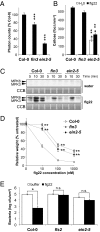
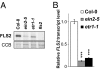
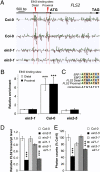
In plant innate immunity, the leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase FLS2 recognizes the bacterial pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) flagellin. The molecular mechanisms underlying PAMP perception are not fully understood. Here, we reveal that the gaseous phytohormone ethylene is an integral part of PAMP-triggered immunity. Plants mutated in the key ethylene-signaling protein EIN2 are impaired in all FLS2-mediated responses, correlating with reduced FLS2 transcription and protein accumulation. The EIN3 and EIN3-like transcription factors, which depend on EIN2 activity for their accumulation, directly control FLS2 expression. Our results reveal a direct role for ethylene in regulation of an innate immune receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zipfel C. Early molecular events in PAMP-triggered immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2009;12:414–420. - PubMed
-
- Boller T, Felix G. A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2009;60:379–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

