TLR4/MyD88-induced CD11b+Gr-1 int F4/80+ non-migratory myeloid cells suppress Th2 effector function in the lung
- PMID: 20664577
- PMCID: PMC2958091
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2010.41
TLR4/MyD88-induced CD11b+Gr-1 int F4/80+ non-migratory myeloid cells suppress Th2 effector function in the lung
Erratum in
- Mucosal Immunol. 2011 Jan;4(1):124
Abstract
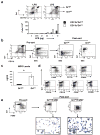
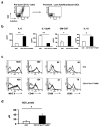
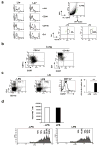
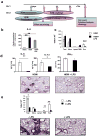
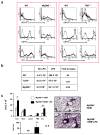
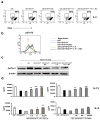
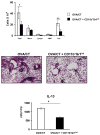
In humans, environmental exposure to a high dose of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) protects from allergic asthma, the immunological underpinnings of which are not well understood. In mice, exposure to a high LPS dose blunted house dust mite-induced airway eosinophilia and T-helper 2 (Th2) cytokine production. Although adoptively transferred Th2 cells induced allergic airway inflammation in control mice, they were unable to do so in LPS-exposed mice. LPS promoted the development of a CD11b(+)Gr1(int)F4/80(+) lung-resident cell resembling myeloid-derived suppressor cells in a Toll-like receptor 4 and myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88)-dependent manner that suppressed lung dendritic cell (DC)-mediated reactivation of primed Th2 cells. LPS effects switched from suppressive to stimulatory in MyD88(-/-) mice. Suppression of Th2 effector function was reversed by anti-interleukin-10 (IL-10) or inhibition of arginase 1. Lineage(neg) bone marrow progenitor cells could be induced by LPS to develop into CD11b(+)Gr1(int)F4/80(+)cells both in vivo and in vitro that when adoptively transferred suppressed allergen-induced airway inflammation in recipient mice. These data suggest that CD11b(+)Gr1(int)F4/80(+) cells contribute to the protective effects of LPS in allergic asthma by tempering Th2 effector function in the tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Shirakawa T, Enomoto T, Shimazu S, Hopkin JM. The inverse association between tuberculin responses and atopic disorder. Science. 1997;275:77–79. - PubMed
-
- Ball TM, et al. Siblings, day-care attendance, and the risk of asthma and wheezing during childhood. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:538–543. - PubMed
-
- Braun-Fahrlander C, et al. Environmental exposure to endotoxin and its relation to asthma in school-age children. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:869–877. - PubMed
-
- Yabuhara A, et al. TH2-polarized immunological memory to inhalant allergens in atopics is established during infancy and early childhood. Clin Exp Allergy. 1997;27:1261–1269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

