A schizophrenia risk gene, ZNF804A, influences neuroanatomical and neurocognitive phenotypes
- PMID: 20664580
- PMCID: PMC2939918
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2010.102
A schizophrenia risk gene, ZNF804A, influences neuroanatomical and neurocognitive phenotypes
Abstract
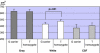
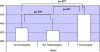
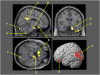
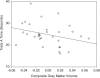
ZNF804A is one of the strongest candidate genes for schizophrenia (SZ), yet its function and role in disease pathophysiology are largely unknown. The only in vivo endophenotype study of the SZ-associated SNP (rs1344706) pointed towards effects on brain functional connectivity. We examined the relationship of this SNP to neuroanatomical and neurocognitive phenotypes that were assessed in healthy individuals. Volunteers with no history of psychiatric illness were assessed with structural magnetic resonance imaging (1.5T GE scanner, standard gradient-echo acquisition). Carriers of the minor allele were compared with homozygotes for the T (SZ-associated) allele on measures of total volume of the white matter (WM), gray matter (GM), and cerebrospinal fluid compartments, as well as on voxel-wise measurements of regional brain volumes. After examining the correlation between genotype-associated regions of interest and neurocognitive performance measures, the effects of rs1344706 genotype on a measure of visuomotor performance speed (trails A) were examined in an independent cohort of volunteers. Among healthy subjects, risk allele homozygotes showed larger total WM volumes than carriers of the other allele. Controlling for WM volumes, these same subjects showed reduced GM volumes in several regions comprising the 'default mode network,' including angular gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, posterior cingulate, and medial orbitofrontal gyrus/gyrus rectus (FDR-corrected p<0.05). The risk allele dosage also predicted impairments on a timed visuomotor performance task (trails A). Results support a role of ZNF804A in phenotypes reflecting altered neural connectivity.
Figures

References
-
- Allen NC, Bagade S, McQueen MB, Ioannidis JP, Kavvoura FK, Khoury MJ, et al. Systematic meta-analyses and field synopsis of genetic association studies in schizophrenia: the SzGene database. Nat Genet. 2008;40:827–834. - PubMed
-
- Aukema EJ, Caan MW, Oudhuis N, Majoie CB, Vos FM, Reneman L, et al. White matter fractional anisotropy correlates with speed of processing and motor speed in young childhood cancer survivors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74:837–843. - PubMed
-
- Bose SK, Mackinnon T, Mehta MA, Turkheimer FE, Howes OD, Selvaraj S, et al. The effect of ageing on grey and white matter reductions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2009;112:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Bueller JA, Aftab M, Sen S, Gomez-Hassan D, Burmeister M, Zubieta JK. BDNF Val66Met allele is associated with reduced hippocampal volume in healthy subjects. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:812–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01MH0084098/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99 MH086756/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH074543/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30MH074543/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH044801/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH060374/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH001760/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR018535/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079800/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH084098/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH044801/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH086756/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR018535/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH080173/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23MH001760/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060374/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH079800/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

