Within-Cluster Resampling for Analysis of Family Data: Ready for Prime-Time?
- PMID: 20664749
- PMCID: PMC2907179
- DOI: 10.4310/sii.2010.v3.n2.a4
Within-Cluster Resampling for Analysis of Family Data: Ready for Prime-Time?
Abstract
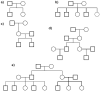
Hoffman et al. [1] proposed an elegant resampling method for analyzing clustered binary data. The focus of their paper was to perform association tests on clustered binary data using within-cluster-resampling (WCR) method. Follmann et al. [2] extended Hoffman et al.'s procedure more generally with applicability to angular data, combining of p-values, testing of vectors of parameters, and Bayesian inference. Follmann et al. [2] termed their procedure multiple outputation because all "excess" data within each cluster is thrown out multiple times. Herein, we refer to this procedure as WCR-MO. For any statistical test to be useful for a particular design, it must be robust, have adequate power, and be easy to implement and flexible. WCR-MO can be easily extended to continuous data and is a computationally intensive but simple and highly flexible method. Considering family as a cluster, one can apply WCR to familial data in genetic studies. Using simulations, we evaluated WCR-MO's robustness for analysis of a continuous trait in terms of type I error rates in genetic research. WCR-MO performed well at the 5% α-level. However, it provided inflated type I error rates for α-levels less than 5% implying the procedure is liberal and may not be ready for application to genetic studies where α levels used are typically much less than 0.05.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erratum: High-Throughput Identification of Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. Tomato in Tomato using Seedling Flood Assay.J Vis Exp. 2023 Oct 18;(200). doi: 10.3791/6576. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37851522
-
Multiple outputation: inference for complex clustered data by averaging analyses from independent data.Biometrics. 2003 Jun;59(2):420-9. doi: 10.1111/1541-0420.00049. Biometrics. 2003. PMID: 12926727
-
Marginal analyses of clustered data when cluster size is informative.Biometrics. 2003 Mar;59(1):36-42. doi: 10.1111/1541-0420.00005. Biometrics. 2003. PMID: 12762439
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Developing Statistical Methods to Improve Stepped-Wedge Cluster Randomized Trials [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 Aug. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 Aug. PMID: 38913814 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Antipsychotic prescribing in youths: a French community-based study from 2006 to 2013.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2015 Oct;24(10):1181-91. doi: 10.1007/s00787-014-0668-y. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25564132
References
-
- Hoffman EB, Sen PK, Weinberg C. Within-cluster resampling. Biometrika. 2001;88:1121–1134.
-
- Follmann D, Proschan M, Leifer E. Multiple outputation: Inference for complex clustered data by averaging analyses from independent data. Biometrics. 2003;59(2):420–9. - PubMed
-
- Meester SG, MacKay J. A parametric model for cluster correlated categorical data. Biometrics. 1994;50(4):954–63. - PubMed
-
- Rieger RH, Weinberg CR. Analysis of clustered binary outcomes using within-cluster paired resampling. Biometrics. 2002;58(2):332–41. - PubMed
-
- Hanley JA, Negassa A, Edwardes MD, Forrester JE. Statistical analysis of correlated data using generalized estimating equations: an orientation. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;157(4):364–75. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous