Topological correction of brain surface meshes using spherical harmonics
- PMID: 20665722
- PMCID: PMC6869946
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21095
Topological correction of brain surface meshes using spherical harmonics
Abstract
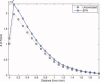
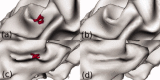
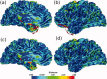
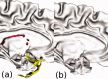
Surface reconstruction methods allow advanced analysis of structural and functional brain data beyond what can be achieved using volumetric images alone. Automated generation of cortical surface meshes from 3D brain MRI often leads to topological defects and geometrical artifacts that must be corrected to permit subsequent analysis. Here, we propose a novel method to repair topological defects using a surface reconstruction that relies on spherical harmonics. First, during reparameterization of the surface using a tiled platonic solid, the original MRI intensity values are used as a basis to select either a "fill" or "cut" operation for each topological defect. We modify the spherical map of the uncorrected brain surface mesh, such that certain triangles are favored while searching for the bounding triangle during reparameterization. Then, a low-pass filtered alternative reconstruction based on spherical harmonics is patched into the reconstructed surface in areas that previously contained defects. Self-intersections are repaired using a local smoothing algorithm that limits the number of affected points to less than 0.1% of the total, and as a last step, all modified points are adjusted based on the T1 intensity. We found that the corrected reconstructions have reduced distance error metrics compared with a "gold standard" surface created by averaging 12 scans of the same brain. Ninety-three percent of the topological defects in a set of 10 scans of control subjects were accurately corrected. The entire process takes 6-8 min of computation time. Further improvements are discussed, especially regarding the use of the T1-weighted image to make corrections.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

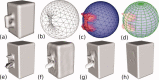
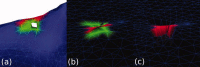
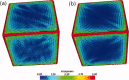
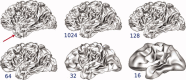


Similar articles
-
Topological correction of brain surface meshes using spherical harmonics.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2009;12(Pt 2):125-32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-04271-3_16. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2009. PMID: 20426104
-
Algorithms to improve the reparameterization of spherical mappings of brain surface meshes.J Neuroimaging. 2011 Apr;21(2):e134-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6569.2010.00484.x. J Neuroimaging. 2011. PMID: 20412393
-
Topological correction of infant white matter surfaces using anatomically constrained convolutional neural network.Neuroimage. 2019 Sep;198:114-124. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.05.037. Epub 2019 May 18. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 31112785 Free PMC article.
-
Development of volume conductor and source models to localize epileptic foci.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007 Apr;24(2):101-19. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e318038fb3e. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17414966 Review.
-
CT artifact correction for sparse and truncated projection data using generative adversarial networks.Med Phys. 2021 Feb;48(2):615-626. doi: 10.1002/mp.14504. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 32996149 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of gestational age with gyrification and neurocognition in healthy adults.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2023 Mar;273(2):467-479. doi: 10.1007/s00406-022-01454-0. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 35904633 Free PMC article.
-
TopoFit: Rapid Reconstruction of Topologically-Correct Cortical Surfaces.Proc Mach Learn Res. 2022 Jul;172:508-520. Proc Mach Learn Res. 2022. PMID: 37220495 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical Areas Associated With Multisensory Integration Showing Altered Morphology and Functional Connectivity in Relation to Reduced Life Quality in Vestibular Migraine.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Aug 16;15:717130. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.717130. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34483869 Free PMC article.
-
Familial Obesity Risk and Current Excess Weight Influence Brain Structure in Adolescents.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2021 Jan;29(1):184-193. doi: 10.1002/oby.23042. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2021. PMID: 33280265 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudo-MRI Engine for MRI-Free Electromagnetic Source Imaging.Hum Brain Mapp. 2025 Feb 1;46(2):e70148. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70148. Hum Brain Mapp. 2025. PMID: 39902833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrams L, Fishkind DE, Priebe CE ( 2002): A proof of the spherical homeomorphism conjecture for surfaces. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21: 1564–1566. - PubMed
-
- Abrams L, Fishkind DE, Priebe CE ( 2004): The generalized spherical homeomorphism theorem for digital images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23: 655–657. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ ( 2005): Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26: 839–851. - PubMed
-
- Ballmaier M, Kumar A, Thompson PM, Narr KL, Lavretsky H, Estanol L, DeLuca H, Toga AW ( 2004): Localizing gray matter deficits in late‐onset depression using computational cortical pattern matching methods. Am J Psychiatry 161: 2091–2099. - PubMed
-
- Bazin P‐L, Pham DL ( 2005a): Topology correction using fast marching methods and its application to brain segmentation In: Duncan J, Gerig G, editors. MICCAI. Palm Springs, CA: Springer; pp 484–491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

