Molecular imaging of angiogenic therapy in peripheral vascular disease with alphanubeta3-integrin-targeted nanoparticles
- PMID: 20665780
- PMCID: PMC2913307
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22447
Molecular imaging of angiogenic therapy in peripheral vascular disease with alphanubeta3-integrin-targeted nanoparticles
Abstract
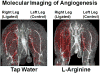
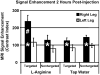
Noninvasive molecular imaging of angiogenesis could play a critical role in the clinical management of peripheral vascular disease patients. The alpha(nu)beta(3)-integrin, a well-established biomarker of neovascular proliferation, is an ideal target for molecular imaging of angiogenesis. This study investigates whether MR molecular imaging with alpha(nu)beta(3)-integrin-targeted perfluorocarbon nanoparticles can detect the neovascular response to angiogenic therapy. Hypercholesterolemic rabbits underwent femoral artery ligation followed by no treatment or angiogenic therapy with dietary L-arginine. MR molecular imaging performed 10 days after vessel ligation revealed increased signal enhancement in L-arginine-treated animals compared to controls. Furthermore, specifically targeted nanoparticles produced two times higher MRI signal enhancement compared to nontargeted particles, demonstrating improved identification of angiogenic vasculature with biomarker targeting. X-ray angiography performed 40 days postligation revealed that L-arginine treatment increased the development of collateral vessels. Histologic staining of muscle capillaries revealed a denser pattern of microvasculature in L-arginine-treated animals, confirming the MR and X-ray imaging results. The clinical application of noninvasive molecular imaging of angiogenesis could lead to earlier and more accurate detection of therapeutic response in peripheral vascular disease patients, enabling individualized optimization for a variety of treatment strategies.
Figures



References
-
- Levy PJ. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of peripheral arterial disease. Clin Cornerstone. 2002;4(5):1–15. - PubMed
-
- Selvin E, Erlinger TP. Prevalence of and risk factors for peripheral arterial disease in the United States: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2000. Circulation. 2004;110(6):738–743. - PubMed
-
- Newman AB, Shemanski L, Manolio TA, Cushman M, Mittelmark M, Polak JF, Powe NR, Siscovick D. Ankle-arm index as a predictor of cardiovascular disease and mortality in the Cardiovascular Health Study. The Cardiovascular Health Study Group. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999;19(3):538–545. - PubMed
-
- Battegay EJ. Angiogenesis: mechanistic insights, neovascular diseases, and therapeutic prospects. J Mol Med. 1995;73(7):333–346. - PubMed
-
- Fam NP, Verma S, Kutryk M, Stewart DJ. Clinician guide to angiogenesis. Circulation. 2003;108(21):2613–2618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

