Involvement of tissue plasminogen activator in stress responsivity during acute cocaine withdrawal in mice
- PMID: 20666641
- PMCID: PMC3832196
- DOI: 10.3109/10253891003786415
Involvement of tissue plasminogen activator in stress responsivity during acute cocaine withdrawal in mice
Abstract
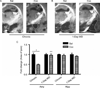
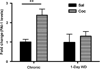
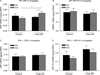
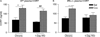
There is evidence that increased release of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) contributes to stress responsivity during cocaine withdrawal (WD). Recent studies suggest that tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) in the CeA is a downstream effector protein for CRF after acute "binge" cocaine administration. The purpose of this study was to determine if tPA modulates cocaine WD-induced stress responsivity. Wild-type (WT) and tPA-deficient (tPA - / - ) mice were subjected to chronic (14 days) "binge" cocaine (45 mg/kg per day) or its acute (1 day) WD. Extracellular tPA activity, CRF mRNA levels, and plasma corticosterone (CORT) levels were measured in tPA - / - and WT mice. Extracellular tPA activity was reduced by 50% in the CeA and medial amygdala of WT mice after chronic cocaine and returned to basal levels after acute WD. Unlike WT mice, tPA - / - mice did not display elevated amygdalar CRF mRNA levels during cocaine WD. In comparison to WT mice, tPA - / - mice showed a blunted plasma CORT response during acute WD. These results demonstrate that tPA activity in the amygdala (Amy) is altered by chronic cocaine exposure, and further suggest an involvement of tPA in modulating amygdalar CRF stress responsive system and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in response to acute cocaine WD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ambrosio E, Sharpe LG, Pilotte NS. Regional binding to corticotropin releasing factor receptors in brain of rats exposed to chronic cocaine and cocaine withdrawal. Synapse. 1997;25:272–276. - PubMed
-
- Aouizerate B, Ho A, Schluger JH, Perret G, Borg L, Le Moal M, Piazza PV, Kreek MJ. Glucocroticoid negative feedback in methadone-maintained former heroin addicts with ongoing cocaine dependence: Dose-response to dexamethasone suppression. Addict Biol. 2006;11:84–96. - PubMed
-
- Bahi A, Dreyer JL. Overexpression of plasminogen activators in the nucleus accumbens enhances cocaine-, amphetamine- and morphine-induced reward and behavioral sensitization. Genes Brain Behav. 2008;7:244–256. - PubMed
-
- Baranes D, Lederfein D, Huang YY, Chen M, Bailey CH, Kandel ER. Tissue plasminogen activator contributes to the late phase of LTP and to synaptic growth in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway. Neuron. 1998;21:813–825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
