Insulin modulates cytokine release and selectin expression in the early phase of allergic airway inflammation in diabetic rats
- PMID: 20667094
- PMCID: PMC2916891
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2466-10-39
Insulin modulates cytokine release and selectin expression in the early phase of allergic airway inflammation in diabetic rats
Abstract
Background: Clinical and experimental data suggest that the inflammatory response is impaired in diabetics and can be modulated by insulin. The present study was undertaken to investigate the role of insulin on the early phase of allergic airway inflammation.
Methods: Diabetic male Wistar rats (alloxan, 42 mg/Kg, i.v., 10 days) and controls were sensitized by s.c. injection of ovalbumin (OA) in aluminium hydroxide 14 days before OA (1 mg/0.4 mL) or saline intratracheal challenge. The following analyses were performed 6 hours thereafter: a) quantification of interleukin (IL)-1beta, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC)-1 in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, b) expression of E- and P- selectins on lung vessels by immunohistochemistry, and c) inflammatory cell infiltration into the airways and lung parenchyma. NPH insulin (4 IU, s.c.) was given i.v. 2 hours before antigen challenge.
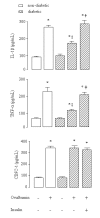
Results: Diabetic rats exhibited significant reduction in the BALF concentrations of IL-1beta (30%) and TNF-alpha (45%), and in the lung expression of P-selectin (30%) compared to non-diabetic animals. This was accompanied by reduced number of neutrophils into the airways and around bronchi and blood vessels. There were no differences in the CINC-1 levels in BALF, and E-selectin expression. Treatment of diabetic rats with NPH insulin, 2 hours before antigen challenge, restored the reduced levels of IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and P-selectin, and neutrophil migration.
Conclusion: Data presented suggest that insulin modulates the production/release of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta, the expression of P- and E-selectin, and the associated neutrophil migration into the lungs during the early phase of the allergic inflammatory reaction.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Insulin Modulates the Immune Cell Phenotype in Pulmonary Allergic Inflammation and Increases Pulmonary Resistance in Diabetic Mice.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 11;11:84. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00084. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117245 Free PMC article.
-
Early phase of allergic airway inflammation in diabetic rats: role of insulin on the signaling pathways and mediators.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;26(4-5):739-48. doi: 10.1159/000322341. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 21063111
-
Modulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung inflammation: Role of insulin.Shock. 2006 Mar;25(3):260-6. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000194042.18699.b4. Shock. 2006. PMID: 16552358
-
Insulin Modulates Liver Function in a Type I Diabetes Rat Model.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(4):1467-79. doi: 10.1159/000430311. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26160428
-
Signaling pathways and mediators in LPS-induced lung inflammation in diabetic rats: role of insulin.Shock. 2010 Jan;33(1):76-82. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181a85ec4. Shock. 2010. PMID: 19373130
Cited by
-
DM-induced Hypermethylation of IR and IGF1R attenuates mast cell activation and airway responsiveness in rats.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Dec;24(24):14381-14391. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16059. Epub 2020 Nov 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33145961 Free PMC article.
-
A Bittersweet Response to Infection in Diabetes; Targeting Neutrophils to Modify Inflammation and Improve Host Immunity.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 3;12:678771. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.678771. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34149714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leukotriene B4-mediated sterile inflammation promotes susceptibility to sepsis in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes.Sci Signal. 2015 Jan 27;8(361):ra10. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005568. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 25628460 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Modulates the Immune Cell Phenotype in Pulmonary Allergic Inflammation and Increases Pulmonary Resistance in Diabetic Mice.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 11;11:84. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00084. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117245 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Modulates Cytokine Release, Collagen and Mucus Secretion in Lung Remodeling of Allergic Diabetic Mice.Front Immunol. 2017 Jun 9;8:633. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00633. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28649241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vianna EO, Garcia-Leme J. Allergen-induced airway inflammation in Rats: role of insulin. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151:809–814. - PubMed
-
- Belmonte KE, Fryer AD, Costello RW. Role of insulin in antigen-induced airway eosinophilia and neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor dysfunction. J Appl Physiol. 1998;85:1708–1718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

