Large-scale analysis of structural, sequence and thermodynamic characteristics of A-to-I RNA editing sites in human Alu repeats
- PMID: 20667096
- PMCID: PMC3091650
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-453
Large-scale analysis of structural, sequence and thermodynamic characteristics of A-to-I RNA editing sites in human Alu repeats
Abstract
Background: Alu repeats in the human transcriptome undergo massive adenosine to inosine RNA editing. This process is selective, as editing efficiency varies greatly among different adenosines. Several studies have identified weak sequence motifs characterizing the editing sites, but these alone do not account for the large diversity observed.
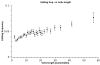
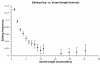
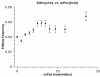
Results: Here we build a dataset of 29,971 editing sites and use it to characterize editing preferences. We focus on structural aspects, studying the double-stranded RNA structure of the Alu repeats, and show the editing frequency of a given site to depend strongly on the micro-structure it resides in. Surprisingly, we find that interior loops, and especially the nucleotides at their edges, are more likely to be edited than helices. In addition, the sequence motifs characterizing editing sites vary with the micro-structure. Finally, we show that thermodynamic stability of the site is important for its editing.
Conclusions: Analysis of a large dataset of editing events reveals more information on sequence and structural motifs characterizing the A-to-I editing process.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alu elements shape the primate transcriptome by cis-regulation of RNA editing.Genome Biol. 2014 Feb 3;15(2):R28. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-2-r28. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 24485196 Free PMC article.
-
A-to-I RNA editing occurs at over a hundred million genomic sites, located in a majority of human genes.Genome Res. 2014 Mar;24(3):365-76. doi: 10.1101/gr.164749.113. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 24347612 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for large diversity in the human transcriptome created by Alu RNA editing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Nov;37(20):6905-15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp729. Epub 2009 Sep 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19740767 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing of non-coding RNA and its role in gene regulation.Biochimie. 2015 Oct;117:22-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.05.020. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 26051678 Review.
-
ALU A-to-I RNA Editing: Millions of Sites and Many Open Questions.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2181:149-162. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0787-9_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32729079 Review.
Cited by
-
A-to-I RNA editing - immune protector and transcriptome diversifier.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Aug;19(8):473-490. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0006-1. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29692414 Review.
-
Evolutionarily significant A-to-I RNA editing events originated through G-to-A mutations in primates.Genome Biol. 2019 Feb 4;20(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1638-y. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 30712515 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation of A-to-I RNA editing in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2017 Mar 10;13(3):e1006648. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006648. eCollection 2017 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28282384 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of exceptionally potent adenosine deaminases RNA editors from high body temperature organisms.PLoS Genet. 2023 Mar 6;19(3):e1010661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010661. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 36877730 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editome in rhesus macaque shaped by purifying selection.PLoS Genet. 2014 Apr 10;10(4):e1004274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004274. eCollection 2014 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24722121 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

