Structures of membrane proteins
- PMID: 20667175
- PMCID: PMC3604715
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033583510000041
Structures of membrane proteins
Abstract
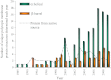
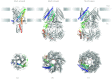
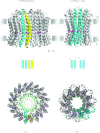
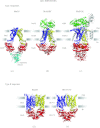
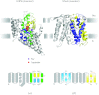
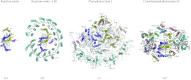
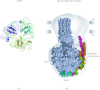
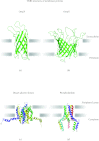
In reviewing the structures of membrane proteins determined up to the end of 2009, we present in words and pictures the most informative examples from each family. We group the structures together according to their function and architecture to provide an overview of the major principles and variations on the most common themes. The first structures, determined 20 years ago, were those of naturally abundant proteins with limited conformational variability, and each membrane protein structure determined was a major landmark. With the advent of complete genome sequences and efficient expression systems, there has been an explosion in the rate of membrane protein structure determination, with many classes represented. New structures are published every month and more than 150 unique membrane protein structures have been determined. This review analyses the reasons for this success, discusses the challenges that still lie ahead, and presents a concise summary of the key achievements with illustrated examples selected from each class.
Figures
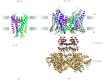
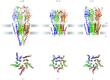





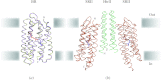

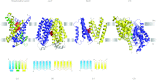
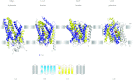

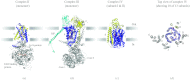
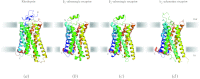

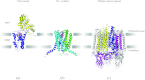


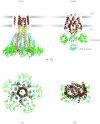
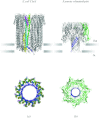

Similar articles
-
Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012).Phys Biol. 2013 Aug;10(4):040301. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/10/4/040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Phys Biol. 2013. PMID: 23912807
-
Methods for measuring the thermodynamic stability of membrane proteins.Methods Enzymol. 2009;455:213-36. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)04208-0. Methods Enzymol. 2009. PMID: 19289208
-
NMR structures of polytopic integral membrane proteins.Mol Membr Biol. 2011 Sep;28(6):370-97. doi: 10.3109/09687688.2011.603100. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Mol Membr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21809901 Review.
-
Structural insights into functional lipid-protein interactions in secondary transporters.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Mar;1850(3):476-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.05.010. Epub 2014 May 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 24859688 Review.
-
Crystal structures of all-alpha type membrane proteins.Eur Biophys J. 2010 Apr;39(5):723-55. doi: 10.1007/s00249-009-0546-6. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Eur Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 19826804 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Fluorescence Recovery after Photobleaching for Decoupling Transport and Kinetics of Biomacromolecules in Cellular Physiology.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 7;14(9):1913. doi: 10.3390/polym14091913. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35567083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An artificial molecular pump.Nat Nanotechnol. 2015 Jun;10(6):547-53. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.96. Epub 2015 May 18. Nat Nanotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25984834
-
Custom Design of a Humidifier Chamber for InMeso Crystallization.Cryst Growth Des. 2023 Dec 12;24(1):325-330. doi: 10.1021/acs.cgd.3c01034. eCollection 2024 Jan 3. Cryst Growth Des. 2023. PMID: 38188264 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of a cholinergic cell membrane.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Aug 23;119(34):e2207641119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2207641119. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35969788 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of membrane proteins in the form of native cell membrane nanoparticles using novel membrane active polymers.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Oct 9;5(21):5932-5940. doi: 10.1039/d3na00381g. eCollection 2023 Oct 24. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 37881706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson J., Smirnova I., Kasho V., Verner G., Kaback H. R.. Iwata S.. Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Science. 2003;301(5633):610–615. & . ( - PubMed
-
- Accardi A.. Miller C.. Secondary active transport mediated by a prokaryotic homologue of ClC Cl- channels. Nature. 2004;427(6977):803–807. & . ( - PubMed
-
- Ago H., Kanaoka Y., Irikura D., Lam B. K., Shimamura T., Aausten K. F.. Miyano M.. Crystal structure of a human membrane protein involved in cysteinyl leukotriene biosynthesis. Nature. 2007;448(7153):609–612. & . ( - PubMed
-
- Agre P.. Aquaporin water channels (Nobel Lecture) Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2004;43(33):4278–4290. ( - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

