Vertebral arteriovenous fistula associated with neurofibromatosis type I misdiagnosed as a giant aneurysm
- PMID: 20667184
- PMCID: PMC3679581
- DOI: 10.1177/159101990000600109
Vertebral arteriovenous fistula associated with neurofibromatosis type I misdiagnosed as a giant aneurysm
Abstract
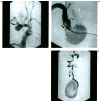
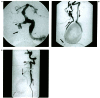
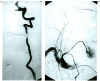
A 59-year-old man with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) presented with bruits and neck pain due to a space occupying lesion in the right neck tissue. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) showed an arteriovenous fistula (AVF) of the right extracranial vertebral artery (VA) with a giant venous pouch and an intracranial berry aneurysm of the right middle cerebral artery (MCA). First, the MCA aneurysm was surgically clipped, then the patient was treated by embolisation with coils. The coils were placed transarterially from the left VA resulting in a partial thrombosis of the venous pouch. Complete closure was achieved secondarily by retrograde transvenous catheterization. Etiology and treatment modalities are discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Deans WR, Bloch S, et al. Arteriovenous fistula in patients with neurofibromatosis. Radiology. 1982;144:103–107. - PubMed
-
- Schievink WI, Piepgras DG. Cervical vertebral aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulae in neurofibromatosis type 1: Case reports. Neurosurgery. 1991;29:760–765. - PubMed
-
- Salyer WR, Salyer DC. The vascular lesions of neurofibromatosis. Angiology. 1974;25:510–519. - PubMed
-
- Greene JF, jr, Fitzwater JE, Burgess J. Arterial lesions associated with neurofibromatosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974;62:481–487. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

