Detection of Unstable Plaques in Patients with Carotid Stenosis using B-Mode Ultrasonography
- PMID: 20667241
- PMCID: PMC3685912
- DOI: 10.1177/15910199000060S125
Detection of Unstable Plaques in Patients with Carotid Stenosis using B-Mode Ultrasonography
Abstract
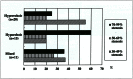
Distal embolism is a detrimental complication of stent placement for the carotid artery stenosis. To evaluate usefulness of B-mode ultrasonography (US) for the detection of unstable plaques in patients with carotid artery stenosis, we examined US in 46 arteries of 35 patients with carotid stenosis of > 30%. The echogenicity of 46 carotid plaques was hyperechoic in 20 plaques, hypoechoic in 15, and mixed-echoic in 11. The echogenicity of carotid plaques was correlated with severity of carotid stenosis, ipsilateral stroke or TIA, heart attack, and risk factors of systemic atherosclerosis. Hypoechoic plaques were associated with severe carotid stenosis and ipsilateral ischemic event. Mixed-echoic plaques had a high incidence of past history of heart attack. Hyperechoic plaques were less likely to associate with risk factors of systemic atherosclerosis. We developed a new method of echodensity analysis. Using a computer software, echodensity values of seven plaque components were determined by comparing US findings and pathology of surgical specimens. The echodensity value was defined as a relative value to the arterial lumen. The calcified part of plaques had the highest echodensity of 6.24 +/- 0.86 (mean +/- 2 S.D.); fibrosis or hyarynoid degeneration of 2.05 +/- 0.40, foamy histiocytes of 1.47 +/- 0.05, necrosis of 1.32 +/- 0.16, cholestelin clefts of 1.28 +/- 0.13, intraplaque hemorrhage of 1.02 +/- 0.09, and intraluminal thrombus of 1.27 +/- 0.07. Constructed from the echodensity value, an echo-densitometry color mapping of the carotid plaque illustrated the exact location and extent of plaque component. B-mode US of carotid plaques represents clinical characteristics relating distal embolism and systemic atherosclerosis. A new method of echodensity analysis and echo-densitometry color mapping of the carotid plaque is useful to detect unstable plaques in patients with carotid stenosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hemispheric symptoms and carotid plaque echomorphology.J Vasc Surg. 2000 Jan;31(1 Pt 1):39-49. doi: 10.1016/s0741-5214(00)70066-8. J Vasc Surg. 2000. PMID: 10642707
-
Ultrasonographic correlates of carotid atherosclerosis in transient ischemic attack and stroke.Stroke. 1995 Apr;26(4):614-9. doi: 10.1161/01.str.26.4.614. Stroke. 1995. PMID: 7709408
-
The effect of B-mode ultrasonic image standardisation on the echodensity of symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid bifurcation plaques.Int Angiol. 1998 Sep;17(3):179-86. Int Angiol. 1998. PMID: 9821032 Clinical Trial.
-
The Risk of Stroke and TIA in Nonstenotic Carotid Plaques: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020 Aug;41(8):1453-1459. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6613. Epub 2020 Jul 9. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020. PMID: 32646945 Free PMC article.
-
B-mode ultrasound and spiral CT for the assessment of carotid atherosclerosis.Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2002 Aug;12(3):421-35. doi: 10.1016/s1052-5149(02)00015-1. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2002. PMID: 12486830 Review.
Cited by
-
Duplex ultrasound findings and clinical outcomes of carotid restenosis after carotid endarterectomy.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 29;15(12):e0244544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244544. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33373383 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants of PTGS2, TXA2R and TXAS1 are associated with carotid plaque vulnerability, platelet activation and TXA2 levels in ischemic stroke patients.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 12;12(7):e0180704. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180704. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28704403 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of SPRR3 in ApoE-/- mice leads to atheroma vulnerability through Akt dependent and independent effects in VSMCs.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 8;12(9):e0184620. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184620. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28886156 Free PMC article.
-
Rationale, Design, and Methodological Aspects of the BUDAPEST-GLOBAL Study (Burden of Atherosclerotic Plaques Study in Twins-Genetic Loci and the Burden of Atherosclerotic Lesions).Clin Cardiol. 2015 Dec;38(12):699-707. doi: 10.1002/clc.22482. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Clin Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26492817 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation and management of plaque protrusion or thrombus following carotid artery stenting.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015;55(2):149-54. doi: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2014-0105. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015. PMID: 25746309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henry M, Amor M, et al. Angioplasty and stenting of the extracranial carotid arteries. J Endovasc Surg. 1998;5:293–302. - PubMed
-
- Roubin GS, Yadav S, et al. Carotid stent-supported angioplasty: a neurovascular intervention to prevent stroke. Am J Cardiol. 1996;78:8–12. - PubMed
-
- Wholey MH, Wholey MH, et al. Cervical carotid artery stent placement. [Review] [28 refs] Semin Intervent Cardiol. 1998;3:105–115. - PubMed
-
- Theron JG, Payelle GG, et al. Carotid artery stenosis: treatment with protected balloon angioplasty and stent placement. Radiology. 1996;201:627–636. - PubMed
-
- Van DH, Trotteur G, et al. Echographic characterization of carotid plaques. Acta Chirur Belg. 1993;93:233–238. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

